12 Mri Abdomen Pelvis Tips For Accurate Diagnosis
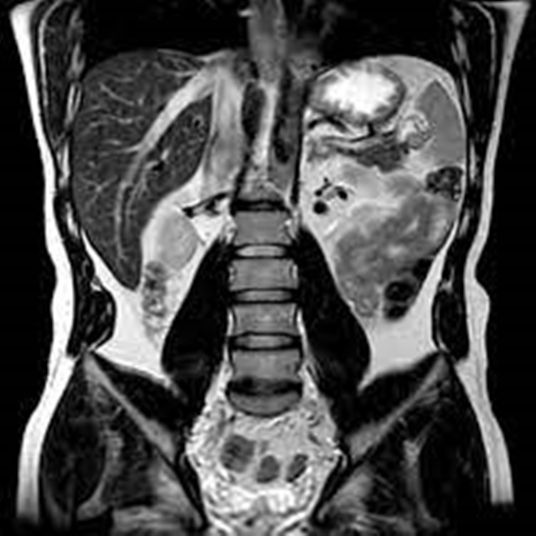
When it comes to accurately diagnosing conditions affecting the abdominal and pelvic regions, Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) of the abdomen and pelvis stands out as a powerful diagnostic tool. This non-invasive procedure offers detailed images of the internal structures, aiding in the detection of a wide range of abnormalities, from organ dysfunction to cancers. Here are 12 expert tips for maximizing the accuracy of MRI abdomen pelvis diagnoses:
Preparation is Key: Proper preparation is crucial for a successful MRI. Patients should be instructed to avoid eating or drinking for a certain period before the scan, depending on the specific requirements of the examination. This helps in reducing artifacts caused by bowel movements and improving the clarity of the images obtained.
Contrast Agents: The use of contrast agents can significantly enhance the visibility of certain structures or lesions within the abdomen and pelvis. Gadolinium-based contrast agents are commonly used for MRI scans, but their administration should be carefully considered, especially in patients with kidney problems, due to the risk of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis.
Sequence Selection: Choosing the right sequences is vital for an accurate diagnosis. For the abdomen and pelvis, T1-weighted and T2-weighted sequences are fundamental. Additionally, sequences like diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) can help in identifying and characterizing lesions, especially in the liver and kidneys.
Respiratory and Cardiac Gating: Movement artifacts from breathing and heartbeats can significantly degrade image quality. Techniques such as respiratory gating or navigator echoes can help compensate for respiratory motion, while cardiac gating can synchronize image acquisition with the cardiac cycle, reducing motion artifacts.
High-Field Strength MRI: When available, high-field strength MRI (such as 3 Tesla machines) offers better spatial resolution and signal-to-noise ratio compared to lower field strength machines. This can be particularly beneficial in detailed assessments of small structures within the abdomen and pelvis.
Multiplanar Reformations: Utilizing multiplanar reformations (MPR) from the acquired data can provide valuable additional information. Reformatted images in the coronal and sagittal planes can offer a better understanding of the spatial relationship between structures and can sometimes reveal lesions that are not as apparent in the standard axial plane.
Clinical Information: Providing the radiologist with detailed clinical information about the patient’s symptoms, medical history, and previous imaging studies can guide the interpretation of the MRI findings. This context is crucial for tailoring the examination to the patient’s specific needs and for making a more accurate diagnosis.
Comparison with Previous Studies: Whenever possible, comparing the current MRI with previous imaging studies (whether MRI, CT, or ultrasound) can help in assessing the evolution of known lesions, detecting new abnormalities, and evaluating the response to treatment.
Focused MRI Examinations: For specific clinical questions, such as evaluating the biliary system or assessing for rectal cancer, focused MRI examinations (like MRCP for the biliary system or MRI of the rectum) can provide detailed, high-resolution images tailored to the area of interest.
Radiologist Experience: The expertise and experience of the radiologist interpreting the MRI are critical. A radiologist with specialized training in abdominal and pelvic imaging can provide more accurate and detailed interpretations, especially in complex cases.
State-of-the-Art Equipment: Regular updates and maintenance of MRI equipment are essential to ensure that the machine is functioning optimally. Newer technologies, such as advanced reconstruction algorithms and improved coil designs, can enhance image quality and diagnostic confidence.
Multidisciplinary Approach: Finally, a multidisciplinary approach involving radiologists, surgeons, oncologists, and other healthcare professionals can facilitate comprehensive patient care. This collaborative environment encourages the sharing of insights and expertise, leading to more accurate diagnoses and effective treatment plans.
By integrating these tips into clinical practice, healthcare providers can optimize the diagnostic potential of MRI abdomen pelvis scans, ultimately leading to better patient outcomes through more accurate and timely diagnoses.
What is the purpose of using contrast agents in MRI scans of the abdomen and pelvis?
+The primary purpose of using contrast agents, such as gadolinium-based compounds, in MRI scans of the abdomen and pelvis is to enhance the visibility of internal structures, lesions, or abnormalities. These agents can highlight differences between various tissues, making it easier for radiologists to detect and characterize conditions such as tumors, inflammation, or vascular diseases.
How does the preparation for an MRI of the abdomen and pelvis differ from other types of MRI scans?
+Preparation for an MRI of the abdomen and pelvis may involve specific dietary restrictions, such as fasting for a certain period, to minimize bowel movement and improve image clarity. Additionally, the use of contrast agents may be more common in abdominal and pelvic MRI scans compared to other types, requiring careful consideration of the patient’s kidney function and potential allergies.
What role does the radiologist’s experience play in the accurate diagnosis of abdominal and pelvic conditions using MRI?
+The experience and specialization of the radiologist are crucial for the accurate interpretation of MRI scans of the abdomen and pelvis. A radiologist with extensive experience in abdominal imaging can provide more precise diagnoses, especially in complex cases, by recognizing subtle abnormalities and understanding the clinical context of the imaging findings.
