12+ Ways Ear Infections Cause Neck Pain Explained
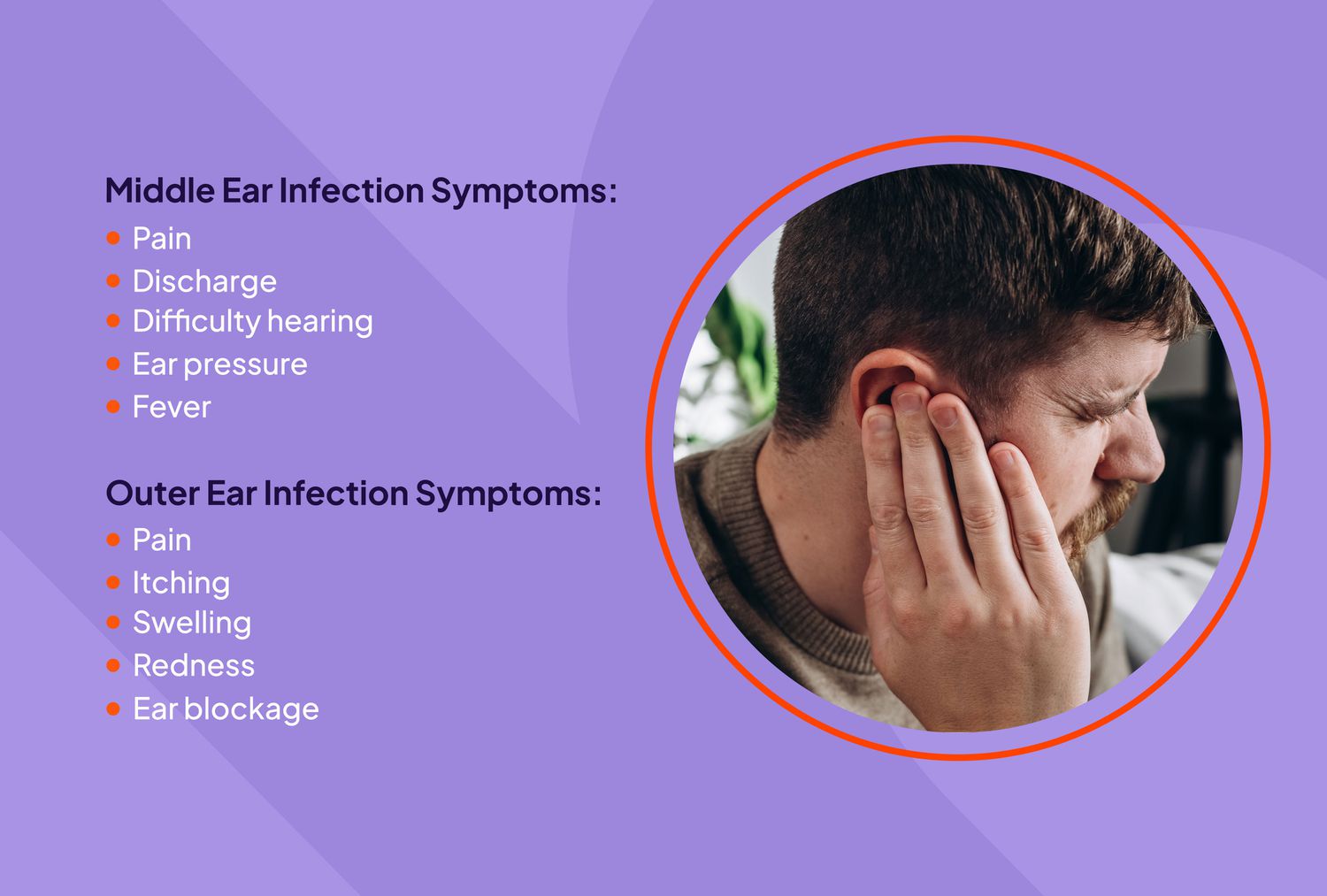
The intricate relationship between ear infections and neck pain is a complex one, involving multiple pathways and mechanisms. While ear infections are often viewed as a localized issue, their effects can reverberate throughout the body, leading to a myriad of symptoms, including neck pain. This response delves into the multifaceted connections between ear infections and neck pain, exploring the various ways in which these conditions interact.
1. Direct Referral of Pain
One of the most straightforward ways ear infections can cause neck pain is through the direct referral of pain. The nerves in the ear are closely linked to those in the neck, and inflammation or infection in the ear can irritate these nerves, leading to pain that is perceived in the neck. This phenomenon is a common example of referred pain, where the source of the pain and its perceived location are not the same.
2. Muscle Tension
Ear infections can lead to muscle tension in the neck and shoulder area. When the body is fighting an infection, it often responds by tensing up, which can lead to muscle spasms and pain. The muscles in the neck are particularly prone to this kind of tension, as they are closely linked to the muscles of the face and head, which can become inflamed or irritated during an ear infection.
3. Lymph Node Involvement
The lymph nodes in the neck can become swollen and tender during an ear infection, leading to neck pain. This swelling is a natural response to the infection, as the body attempts to fight off the invading pathogens. However, it can also lead to discomfort and pain in the neck, especially when swallowing or turning the head.
4. Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
The Eustachian tube connects the middle ear to the back of the throat and helps to regulate air pressure in the ear. During an ear infection, this tube can become blocked or dysfunctional, leading to a buildup of fluid in the ear. This can cause pain not only in the ear but also in the neck, as the Eustachian tube is surrounded by muscles and nerves that can become irritated.
5. Inflammation and Swelling
Inflammation and swelling associated with ear infections can spread to the surrounding areas, including the neck. This can lead to pain, stiffness, and limited mobility in the neck, as the inflamed tissues press against nerves and muscles.
6. Posture Changes
Individuals with ear infections might alter their posture in an attempt to alleviate their discomfort, which can lead to strain on the neck muscles and subsequent pain. For example, tilting the head to one side or leaning forward can put unnecessary strain on the neck, exacerbating any existing pain.
7. Cervicogenic Pain
Cervicogenic pain refers to pain that is referred from the cervical spine (neck) to other areas, including the ear. While this is typically associated with neck problems, an ear infection can sometimes trigger or exacerbate cervicogenic pain pathways, leading to a complex interplay of neck and ear pain.
8. Mastoiditis
In severe cases, an ear infection can spread to the mastoid bone, located behind the ear, leading to a condition known as mastoiditis. This can cause pain that radiates to the neck, among other symptoms, due to the proximity of the mastoid bone to the neck and its associated structures.
9. Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) Dysfunction
The TMJ connects the jawbone to the skull, and dysfunction in this joint can be both a cause and a consequence of ear infections. TMJ issues can lead to pain in the jaw, face, and neck, creating a complex pain profile that includes neck pain as a significant component.
10. Psychological Factors
The psychological impact of dealing with chronic or recurrent ear infections should not be underestimated. Stress, anxiety, and frustration can all contribute to muscle tension, including in the neck, thereby exacerbating neck pain.
11. Sleep Disturbances
Ear infections can lead to sleep disturbances due to pain and discomfort. Poor sleep quality or duration can then contribute to increased muscle tension and pain sensitivity, including in the neck, creating a vicious cycle.
12. Systemic Infection
In rare but serious cases, an ear infection can spread systemically, affecting other parts of the body. This can lead to a generalized feeling of illness, including fever, fatigue, and body aches, which can include neck pain.
Implementing Strategic Relief Measures
Given the complex interplay between ear infections and neck pain, addressing both conditions simultaneously is crucial. This might involve a combination of medical treatments for the ear infection, such as antibiotics, and measures to alleviate neck pain, including physical therapy, pain management strategies, and lifestyle adjustments to reduce stress and improve sleep quality.
Decision Framework for Managing Ear Infections and Neck Pain
- Assessment: Evaluate the severity of the ear infection and the extent of neck pain.
- Medical Intervention: Seek appropriate medical treatment for the ear infection.
- Pain Management: Implement strategies to manage neck pain, including medication, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes.
- Prevention: Adopt preventive measures to reduce the risk of future ear infections, such as practicing good hygiene, avoiding exposure to known irritants, and ensuring prompt treatment of any infections.
Conclusion
The relationship between ear infections and neck pain is nuanced, involving direct and indirect mechanisms that can lead to significant discomfort and distress. Understanding these connections is key to developing effective strategies for managing both conditions. By acknowledging the multifaceted nature of this relationship and adopting a comprehensive approach to treatment and prevention, individuals can better navigate the challenges posed by ear infections and associated neck pain.
Can ear infections cause long-term neck pain?
+Yes, if left untreated or improperly managed, ear infections can lead to chronic conditions that may result in long-term neck pain. It's crucial to address ear infections promptly and effectively to prevent such outcomes.
How can I alleviate neck pain caused by an ear infection?
+Alleviating neck pain caused by an ear infection involves treating the infection itself, using pain management strategies such as over-the-counter pain relievers, applying heat or cold packs to the affected area, and maintaining good posture to reduce strain on the neck.
Is there a connection between ear infections and neck stiffness?
+Yes, ear infections can lead to neck stiffness due to inflammation, muscle tension, and the body's response to the infection. Addressing the underlying infection and using targeted exercises or physical therapy can help relieve stiffness.
In conclusion, the intricate relationship between ear infections and neck pain underscores the importance of comprehensive care and management. By understanding the various pathways through which ear infections can cause neck pain, individuals and healthcare providers can work together to develop effective treatment strategies that address both the infection and its broader effects on the body. This approach not only alleviates current symptoms but also prevents long-term complications, promoting overall well-being and quality of life.

