Autism Epicanthal Folds: Diagnosis And Treatment Options
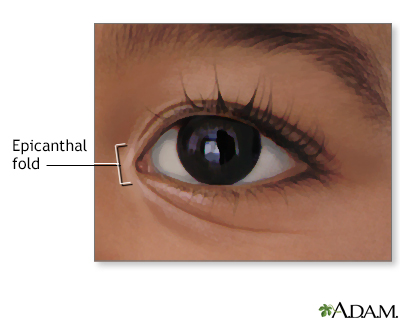
The relationship between autism and epicanthal folds has been a subject of interest in the medical community, particularly in the context of diagnosis and treatment options. Epicanthal folds, which are skin folds of the upper eyelid that cover the inner corner of the eye, are a common feature in individuals with autism spectrum disorder (ASD). While the presence of epicanthal folds is not a definitive diagnostic criterion for autism, it can be an important consideration in the diagnostic process.
Understanding Epicanthal Folds in Autism
Research has shown that individuals with autism are more likely to have epicanthal folds than the general population. A study published in the Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders found that approximately 40% of individuals with autism had epicanthal folds, compared to around 10% of the general population. However, it’s essential to note that the presence of epicanthal folds does not necessarily mean an individual has autism, as these facial features can also be present in individuals without the condition.
Diagnostic Considerations
When diagnosing autism, healthcare professionals consider a range of factors, including behavioral characteristics, cognitive abilities, and physical features. Epicanthal folds can be an important consideration in the diagnostic process, particularly when combined with other physical features such as a broad face, short nose, and prominent jaw. However, it’s crucial to remember that diagnosis should always be based on a comprehensive evaluation of an individual’s unique characteristics, rather than a single feature.
Treatment Options for Autism
While there is no cure for autism, various treatment options can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. These may include:
- Behavioral therapy: Techniques such as applied behavior analysis (ABA) and positive behavioral supports (PBS) can help individuals with autism develop social, communication, and adaptive skills.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), can help alleviate symptoms of anxiety, depression, and hyperactivity in individuals with autism.
- Speech and language therapy: Targeted interventions can help individuals with autism develop communication skills, such as speech, language, and social interaction.
- Occupational therapy: Occupational therapists can help individuals with autism develop daily living skills, such as self-care, feeding, and dressing.
Addressing Epicanthal Folds
In some cases, individuals with autism and epicanthal folds may choose to undergo surgical correction to improve the appearance of their eyes. However, this should always be done in consultation with a qualified healthcare professional and with careful consideration of the potential benefits and risks.
Future Directions
Research into the relationship between autism and epicanthal folds is ongoing, and further studies are needed to fully understand the significance of this feature in autism diagnosis and treatment. As our understanding of autism and its associated features continues to evolve, it’s likely that we will see the development of new diagnostic tools and treatment options that take into account the complex interplay between physical and behavioral characteristics.
Can epicanthal folds be a definitive diagnostic criterion for autism?
+No, epicanthal folds are not a definitive diagnostic criterion for autism. While they can be a common feature in individuals with autism, diagnosis should always be based on a comprehensive evaluation of an individual's unique characteristics.
Can surgical correction of epicanthal folds improve symptoms of autism?
+No, surgical correction of epicanthal folds is not a treatment for autism. While it may improve the appearance of the eyes, it will not address the underlying symptoms of autism.
What are the most effective treatment options for autism?
+The most effective treatment options for autism typically involve a combination of behavioral therapy, medications, speech and language therapy, and occupational therapy. The specific treatment plan will depend on the individual's unique needs and characteristics.
In conclusion, while epicanthal folds can be an important consideration in autism diagnosis, they are just one piece of the puzzle. By taking a comprehensive approach to diagnosis and treatment, healthcare professionals can help individuals with autism and their families develop effective strategies for managing symptoms and improving quality of life.


