Bohr Model Of Carbon Atom
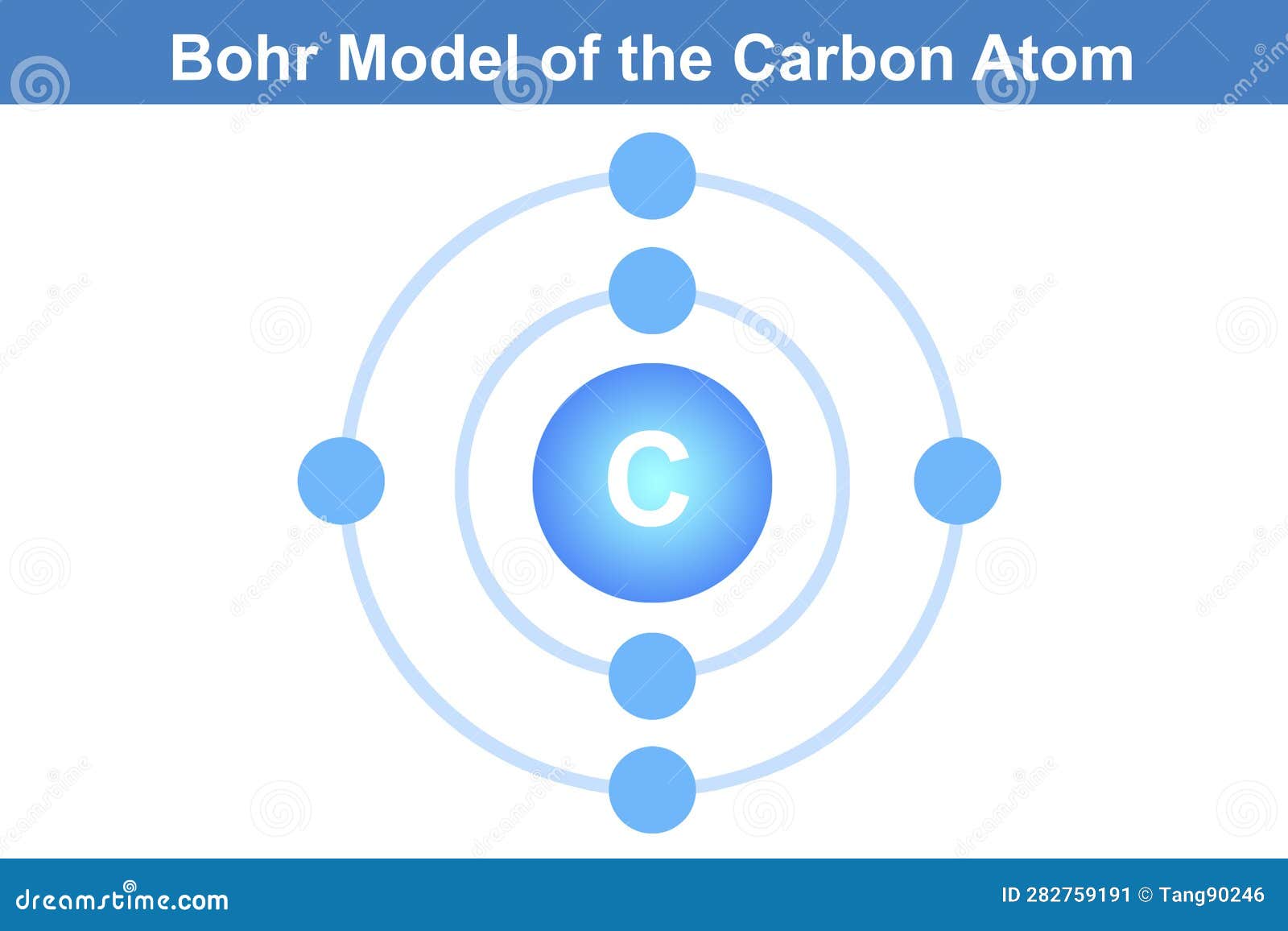
The Bohr model of the carbon atom is a fundamental concept in chemistry and physics that helps us understand the structure and behavior of atoms. In this article, we will delve into the details of the Bohr model of the carbon atom, exploring its components, how it works, and its significance in understanding the properties of carbon.
To begin with, let’s consider the basic structure of an atom. Atoms are the building blocks of matter, and they consist of three main components: protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons and neutrons are found in the nucleus, which is the central part of the atom, while electrons orbit around the nucleus. The carbon atom, specifically, has six protons, six neutrons, and six electrons.
The Bohr model, proposed by Niels Bohr in 1913, is a simplified representation of the atom that helps us visualize and understand the arrangement of electrons in an atom. According to the Bohr model, electrons occupy specific energy levels, or shells, around the nucleus. These energy levels are quantized, meaning that electrons can only occupy specific energy states and not any energy state in between.
In the case of the carbon atom, the six electrons occupy the first and second energy levels. The first energy level, also known as the 1s orbital, can hold up to two electrons, and the second energy level, also known as the 2s and 2p orbitals, can hold up to eight electrons. The electronic configuration of carbon is 1s² 2s² 2p², indicating that two electrons occupy the 1s orbital, two electrons occupy the 2s orbital, and two electrons occupy the 2p orbital.
Now, let’s take a closer look at the energy levels in the carbon atom. The 1s orbital is the lowest energy level and is closest to the nucleus. The 2s orbital is the next energy level and is higher in energy than the 1s orbital. The 2p orbital is also part of the second energy level and has a slightly higher energy than the 2s orbital.
One of the key features of the Bohr model is the concept of electron spin. Electron spin refers to the intrinsic angular momentum of an electron, which causes it to behave like a tiny magnet. In the carbon atom, the electrons in the 1s and 2s orbitals have paired spins, meaning that they spin in opposite directions. The electrons in the 2p orbital have unpaired spins, meaning that they spin in the same direction.
The Bohr model of the carbon atom has several implications for our understanding of the chemical properties of carbon. For example, the electronic configuration of carbon explains why it forms four covalent bonds with other atoms. The four unpaired electrons in the 2p orbital are available for bonding, allowing carbon to form stable molecules with other elements.
In conclusion, the Bohr model of the carbon atom provides a fundamental understanding of the structure and behavior of atoms. By visualizing the arrangement of electrons in energy levels, we can gain insights into the chemical properties of carbon and other elements. While the Bohr model has limitations and has been largely superseded by more advanced models, such as the quantum mechanical model, it remains an essential tool for understanding the basics of atomic structure and chemistry.
What is the electronic configuration of the carbon atom?
+The electronic configuration of the carbon atom is 1s² 2s² 2p², indicating that two electrons occupy the 1s orbital, two electrons occupy the 2s orbital, and two electrons occupy the 2p orbital.
What is the significance of the Bohr model in understanding the chemical properties of carbon?
+The Bohr model provides a framework for understanding the chemical properties of carbon, including its ability to form four covalent bonds with other atoms. The electronic configuration of carbon explains why it forms stable molecules with other elements.
What are the limitations of the Bohr model in describing the behavior of atoms?
+The Bohr model has several limitations, including its inability to account for the Zeeman effect, the fine structure of spectral lines, and the behavior of atoms in magnetic fields. The model has been largely superseded by more advanced models, such as the quantum mechanical model.
The Bohr model of the carbon atom is a fundamental concept in chemistry and physics that has had a profound impact on our understanding of the structure and behavior of atoms. By exploring the components of the Bohr model, including the arrangement of electrons in energy levels and the concept of electron spin, we can gain insights into the chemical properties of carbon and other elements. While the model has limitations, it remains an essential tool for understanding the basics of atomic structure and chemistry.


