Dalton In G Mol: Calculate Molecular Weight Accurately
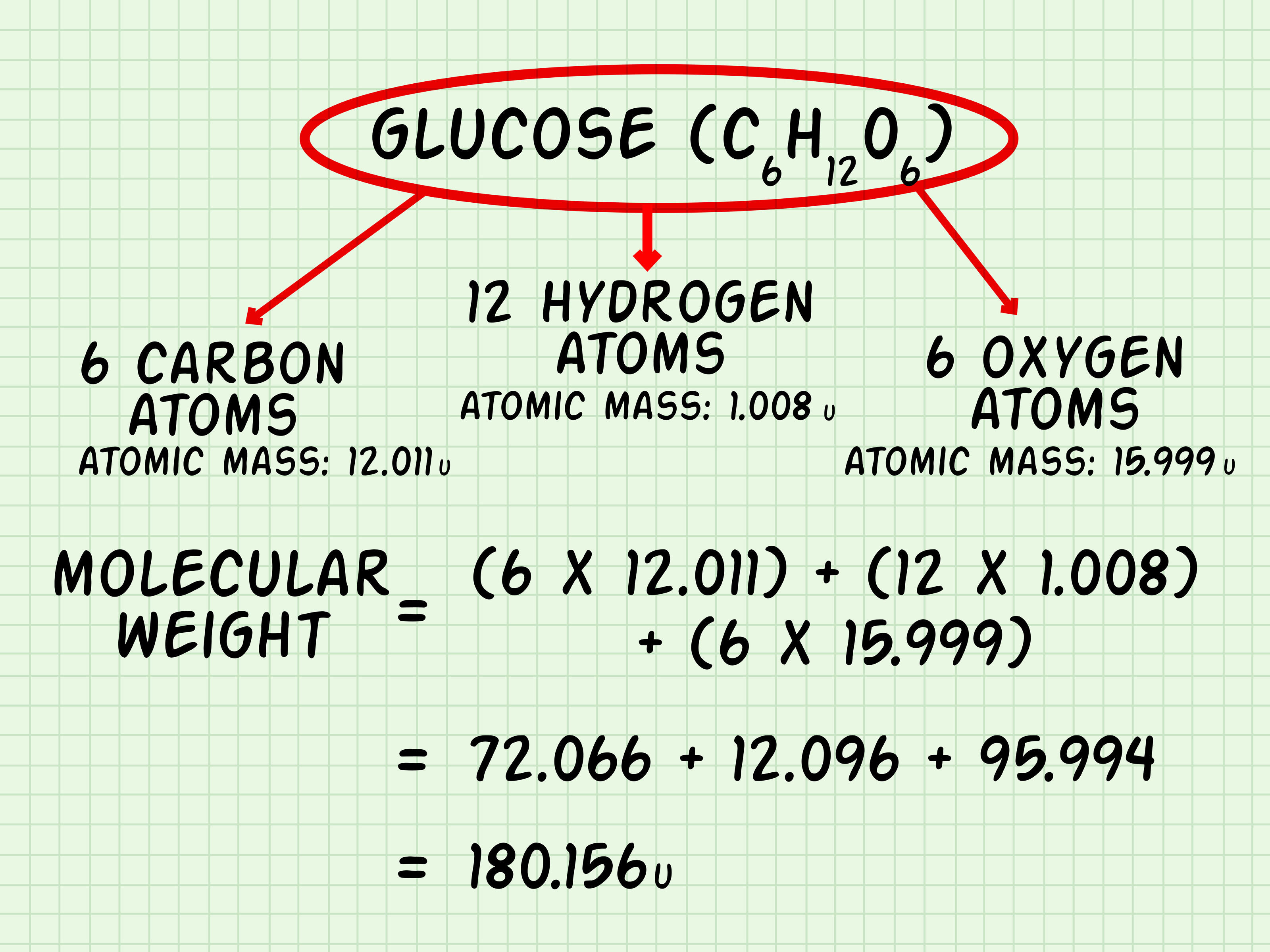
The calculation of molecular weight is a fundamental concept in chemistry, crucial for understanding the properties and behaviors of molecules. Molecular weight, also known as molecular mass, is the sum of the atomic weights of the atoms in a molecule. It is expressed in units of dalton (Da) or grams per mole (g/mol). In this article, we will delve into the details of calculating molecular weight accurately, exploring the steps, considerations, and tools involved in this process.
Understanding Atomic Weight
Before calculating molecular weight, it’s essential to understand atomic weight. Atomic weight is the average mass of an atom of an element, taking into account its naturally occurring isotopes. The atomic weights of elements are typically provided on the periodic table and are used as the basis for calculating molecular weights.
Steps to Calculate Molecular Weight
Calculating molecular weight involves summing the atomic weights of all atoms in a molecule. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Identify the Molecular Formula: The first step is to know the molecular formula of the compound, which tells you how many atoms of each element are present in one molecule of the compound.
- Find Atomic Weights: Look up the atomic weights of each element present in the molecule from a reliable source, such as the periodic table.
- Calculate the Total Weight: Multiply the atomic weight of each element by the number of atoms of that element in the molecule, then sum these values.
Example Calculation
Let’s calculate the molecular weight of water (H₂O) as an example:
- The molecular formula of water is H₂O, meaning one molecule of water contains 2 hydrogen atoms and 1 oxygen atom.
- The atomic weight of hydrogen (H) is approximately 1.00794 Da, and the atomic weight of oxygen (O) is approximately 15.9994 Da.
- Calculate the molecular weight: (2 * 1.00794) + 15.9994 = 2.01588 + 15.9994 = 18.01528 Da.
Considerations for Accuracy
Several factors can affect the accuracy of molecular weight calculations:
- Isotopic Variation: The presence of different isotopes of an element can affect its average atomic weight. For most calculations, the standard atomic weights provided on the periodic table are sufficient, but in precise work, isotopic masses may need to be considered.
- Rounding Errors: Rounding atomic weights during calculation can lead to small errors in the final molecular weight. It’s best to carry more decimal places until the final calculation to minimize this effect.
- Source of Atomic Weights: Ensure that atomic weights are taken from a reliable and up-to-date source. The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) provides standardized atomic weights that should be used for consistency.
Tools for Molecular Weight Calculation
While manual calculation is straightforward for simple molecules, it can become cumbersome for larger, more complex molecules. Several tools and software programs are available to simplify and accelerate molecular weight calculations, including:
- Online Molecular Weight Calculators: Numerous websites offer molecular weight calculators where you can input the molecular formula and get the molecular weight instantly.
- Chemistry Software: Programs like ChemDraw, MarvinSketch, and Pybel allow you to draw molecular structures and calculate their molecular weights based on the drawn structure.
Conclusion
Calculating molecular weight is a fundamental skill in chemistry, essential for a wide range of applications from synthesis to analytical chemistry. By following the steps outlined and considering the factors that affect accuracy, you can ensure precise calculations. Whether you’re a student, researcher, or professional in the field, understanding and accurately calculating molecular weight is crucial for advancing knowledge and applications in chemistry.
FAQ Section
What is the difference between molecular weight and molar mass?
+Molecular weight and molar mass are often used interchangeably, but technically, molecular weight refers to the weight of a single molecule, while molar mass is the weight of one mole of molecules. However, the numerical value for both is the same when expressed in g/mol or Da.
How do I calculate the molecular weight of a polymer?
+For polymers, you calculate the molecular weight of the repeating unit (monomer) and then multiply by the number of repeating units (n) to get the total molecular weight of the polymer chain. The formula is: Molecular weight of polymer = n * Molecular weight of monomer.
What are the units used for expressing molecular weight?
+Molecular weight is typically expressed in units of dalton (Da) or grams per mole (g/mol). These units are equivalent in terms of numerical value but differ in context; dalton is used for the mass of a single molecule, while g/mol (molar mass) refers to the mass of one mole of molecules.
Advanced Calculation Scenarios
For complex molecules, including polymers and biomolecules like proteins and nucleic acids, calculating molecular weight can be more complicated due to the large number of atoms involved and the variability in their composition. In such cases, using computational tools and software can significantly simplify the process. Additionally, understanding the chemical structure and the repeating units in polymers or the sequence of amino acids in proteins can help in accurately determining their molecular weights.
Future Directions
Advancements in analytical chemistry and computational power continue to enhance our ability to calculate and utilize molecular weights with greater precision. Techniques like mass spectrometry allow for the direct measurement of molecular weights of complex molecules, providing valuable data for research and applications. As our understanding of molecular interactions and properties deepens, the importance of accurate molecular weight calculations will only continue to grow, driving further innovations in this field.
By mastering the calculation of molecular weight, chemists and researchers can better understand the properties of substances, design new materials, and advance our knowledge of chemical and biological processes. Whether through traditional manual calculations or leveraging advanced computational tools, the ability to accurately determine molecular weight remains a cornerstone of chemical research and development.


