Dat Biology Questions
Understanding the intricacies of biology can be a fascinating journey, filled with complex processes, incredible diversity, and the pursuit of discovering how life functions at its core. From the tiniest microorganisms to the mightiest trees and the complexity of human bodies, biology encompasses a vast range of topics. Here, we’ll delve into some of the most compelling aspects of biology, exploring both fundamental concepts and the latest breakthroughs in the field.
The Building Blocks of Life: Cells
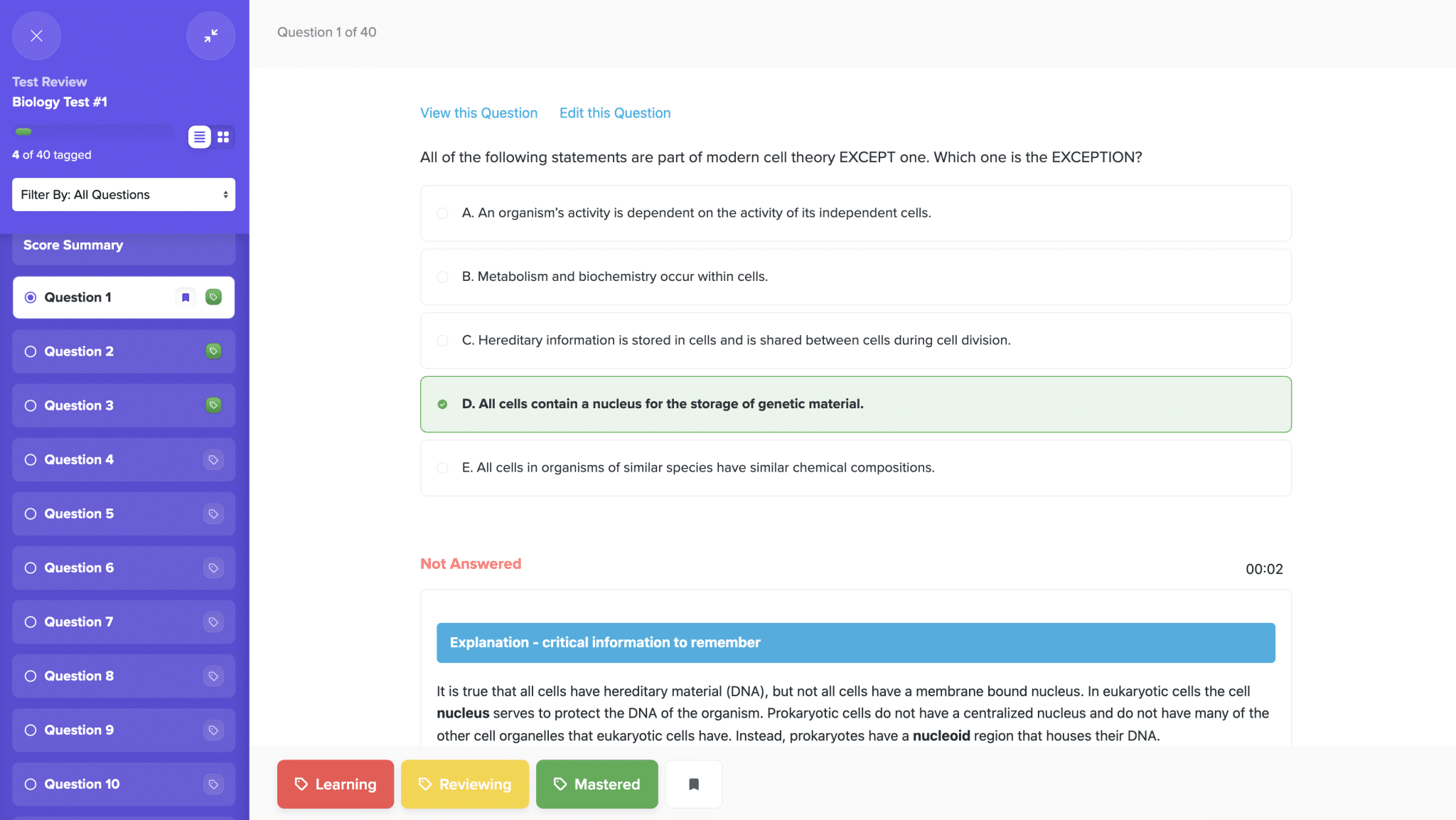
At the heart of biology lies the cell, the smallest unit of life. Cells are incredibly diverse, ranging from simple bacterial cells to the highly specialized cells found in humans and other complex organisms. The cell theory, which states that all living things are composed of one or more cells, that cells are the basic units of life, and that all cells arise from existing cells, forms the foundation of modern biology.
Cellular Structure and Function
Cells consist of several key components, including the cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, and various organelles, each with specific functions. The cell membrane, a thin layer of lipid and protein molecules, controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell. The cytoplasm, where many metabolic reactions occur, is the region between the cell membrane and the nucleus. The nucleus, often referred to as the control center of a cell, contains most of the cell’s genetic material in the form of DNA.
Cellular Processes: Metabolism and Division
Cellular metabolism refers to the chemical reactions that occur within cells to sustain life. These reactions can be categorized into two main types: catabolism, the process of breaking down molecules to release energy, and anabolism, the process of using energy to build complex molecules from simpler ones. Another crucial cellular process is cell division, which allows cells to reproduce. There are two types of cell division: mitosis, which results in two daughter cells genetically identical to the parent cell, and meiosis, which produces four non-identical sex cells (sperm or eggs) with half the number of chromosomes of the parent cell.
Genetics: The Code of Life
Genetics, the study of heredity and variation, is fundamental to understanding how traits are passed from one generation to the next. The discovery of the DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) structure by James Watson and Francis Crick revealed the genetic code, which is written in the sequence of four chemical bases - adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine ©, and thymine (T) - that make up an organism’s DNA. This code determines the genetic instructions used in the development and function of all living organisms.
Genetic Inheritance and Variation
Genetic inheritance refers to the passing of traits from parents to their offspring through the transmission of genetic information. This process is governed by Mendel’s laws of inheritance, which describe how genes are inherited in a predictable manner. Genetic variation, which arises from mutations, gene flow, and genetic recombination during meiosis, is essential for the survival and adaptation of species. It provides the raw material for natural selection, allowing populations to evolve over time in response to changing environments.
Evolution: The History of Life on Earth
Evolution, the scientifically supported theory that all species of life have developed from a common ancestor through the process of variation, mutation, genetic drift, and natural selection, underpins our understanding of biology. The history of life on Earth, as documented by the fossil record and comparative anatomy, shows a gradual progression from simple, single-celled organisms to complex, multicellular life forms.
Mechanisms of Evolution
Natural selection, a key driver of evolution, is the process by which individuals with certain traits that are better suited to their environment are more likely to survive and reproduce, thus passing those traits on to the next generation. Other mechanisms, such as genetic drift, mutation, and gene flow, also contribute to the evolution of species by altering the genetic makeup of populations over time.
Ecology: The Interconnectedness of Life
Ecology, the study of the relationships between living organisms and their environment, highlights the interconnectedness of life on Earth. Ecosystems, which consist of all the living organisms (biotic factors) in a given area, interacting with each other, and with their non-living environments (abiotic factors), are complex systems that support a vast array of life.
Ecosystem Balance and Conservation
Maintaining the balance of ecosystems is crucial for the health of the planet. Human activities, such as deforestation, pollution, and overfishing, can disrupt this balance, leading to biodiversity loss and ecosystem degradation. Conservation efforts, including the protection of natural habitats, the restoration of degraded ecosystems, and the management of resources in a sustainable manner, are essential for preserving the integrity of ecosystems and ensuring the long-term survival of species.
Practical Applications of Biology
Biology has numerous practical applications that impact our daily lives. In medicine, understanding biological processes and the genetic basis of diseases has led to the development of new treatments and therapies. In agriculture, knowledge of genetics, ecology, and plant biology has improved crop yields and disease resistance. Furthermore, advances in biotechnology have opened up new avenues for the production of biofuels, bioproducts, and pharmaceuticals.
Biotechnology: The Future of Biological Science
Biotechnology, which involves the use of biological systems, living organisms, or derivatives thereof, to develop new products and technologies, holds great promise for solving some of the world’s most pressing challenges. From the development of vaccines and medicines to the creation of genetically modified crops that can thrive in challenging environments, biotechnology is at the forefront of innovation in the biological sciences.
Conclusion
Biology, with its vast scope and intricate details, is a field that continues to captivate scientists and the general public alike. As our understanding of biological processes deepens, so does our ability to address global challenges, improve human health, and conserve the natural world. The journey of discovery in biology is ongoing, with new findings and technologies emerging regularly, offering insights into the workings of life and our place within the larger web of existence.
What is the basic unit of life in biology?
+The cell is considered the basic unit of life in biology. All living organisms are composed of one or more cells, and cells are the smallest units that can be considered alive.
What is the genetic code, and why is it important?
+The genetic code is the set of rules used by living cells to translate information encoded within genetic material (DNA or RNA sequences) into proteins. It is crucial because it determines the genetic instructions used in the development and function of all living organisms.
How does evolution occur?
+Evolution occurs through several mechanisms, including natural selection, genetic drift, mutation, and gene flow. These processes alter the genetic makeup of populations over time, allowing them to adapt to changing environments and eventually giving rise to new species.
In the realm of biology, the pursuit of knowledge is endless, with each discovery opening doors to new questions and opportunities for exploration. As we continue to unravel the mysteries of life, we not only deepen our understanding of the natural world but also empower ourselves with the knowledge needed to address the challenges of the future.


