Diabetic Cat Glucose Range
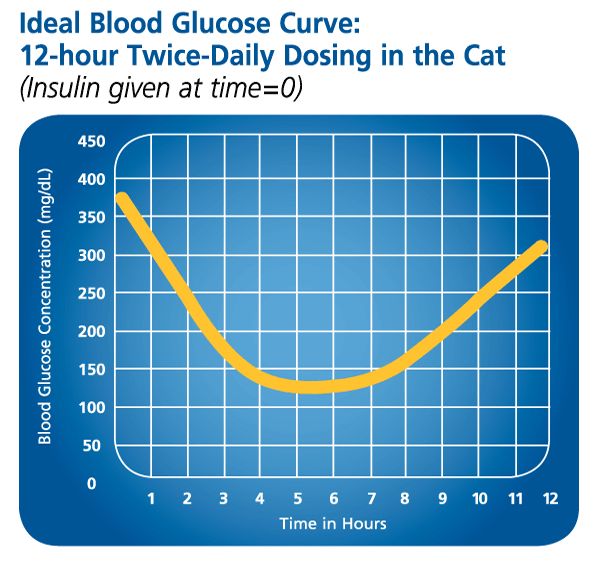
Managing diabetes in cats requires careful monitoring of their blood glucose levels to ensure they remain within a healthy range. Unlike humans, cats have a unique physiological response to diabetes, and their glucose levels can fluctuate significantly. Understanding the normal and diabetic glucose ranges in cats is crucial for effective management of the disease.
Normal Glucose Range in Cats: The normal blood glucose range in cats is between 60-120 mg/dL. However, this range can vary slightly depending on the laboratory, the method of testing, and the individual cat’s health status. It’s essential to consult with a veterinarian to determine the normal glucose range for a specific cat.
Diabetic Glucose Range in Cats: Cats with diabetes often have elevated blood glucose levels, which can range from 200-500 mg/dL or higher. The American Animal Hospital Association (AAHA) recommends the following glucose ranges for diabetic cats:
- Mild hyperglycemia: 180-250 mg/dL
- Moderate hyperglycemia: 251-350 mg/dL
- Severe hyperglycemia: 351-500 mg/dL
- Critical hyperglycemia: >500 mg/dL
Importance of Monitoring Glucose Levels: Regular monitoring of glucose levels is crucial in diabetic cats to:
- Adjust insulin doses: Glucose levels help determine the optimal insulin dose to manage the cat’s diabetes.
- Prevent hypoglycemia: Monitoring glucose levels helps prevent hypoglycemia (low blood sugar), which can be life-threatening.
- Detect hyperglycemia: Regular monitoring helps detect high blood sugar levels, which can lead to complications such as diabetic ketoacidosis.
- Evaluate treatment efficacy: Glucose levels help assess the effectiveness of the current treatment plan and make adjustments as needed.
Methods for Monitoring Glucose Levels: There are several methods for monitoring glucose levels in diabetic cats, including:
- Blood glucose meters: Portable meters that measure blood glucose levels from a small blood sample.
- Continuous glucose monitoring systems: Devices that track glucose levels continuously over a period.
- Urine glucose tests: Tests that measure glucose levels in the urine.
- Fructosamine tests: Blood tests that measure average glucose levels over the past 2-3 weeks.
Factors Affecting Glucose Levels in Diabetic Cats: Several factors can influence glucose levels in diabetic cats, including:
- Insulin dose and timing: The amount and timing of insulin administration can impact glucose levels.
- Diet: The type and amount of food consumed can affect glucose levels.
- Exercise: Physical activity can lower glucose levels.
- Stress: Stress can increase glucose levels.
- Other health conditions: Concurrent health conditions, such as kidney disease or hyperthyroidism, can impact glucose levels.
Frequent Glucose Monitoring: Frequent glucose monitoring is essential for diabetic cats, especially during the initial treatment period. The frequency of monitoring may vary depending on the individual cat’s needs, but it’s common to monitor glucose levels:
- Before meals: To determine the optimal insulin dose.
- After meals: To evaluate the cat’s response to food and insulin.
- At bedtime: To ensure glucose levels are within a safe range overnight.
What is the ideal glucose range for a diabetic cat?
+The ideal glucose range for a diabetic cat is between 100-250 mg/dL. However, this range may vary depending on the individual cat's needs and the veterinarian's recommendations.
How often should I monitor my diabetic cat's glucose levels?
+The frequency of glucose monitoring depends on the individual cat's needs and the veterinarian's recommendations. It's common to monitor glucose levels 2-4 times a day, especially during the initial treatment period.
What are the consequences of uncontrolled diabetes in cats?
+Uncontrolled diabetes in cats can lead to severe complications, including diabetic ketoacidosis, kidney disease, and nerve damage. It's essential to work with a veterinarian to develop an effective treatment plan and monitor glucose levels regularly.
By understanding the diabetic cat glucose range and monitoring glucose levels regularly, cat owners can work with their veterinarians to develop an effective treatment plan and improve their cat’s quality of life.

