Discounted Cash Flow Table
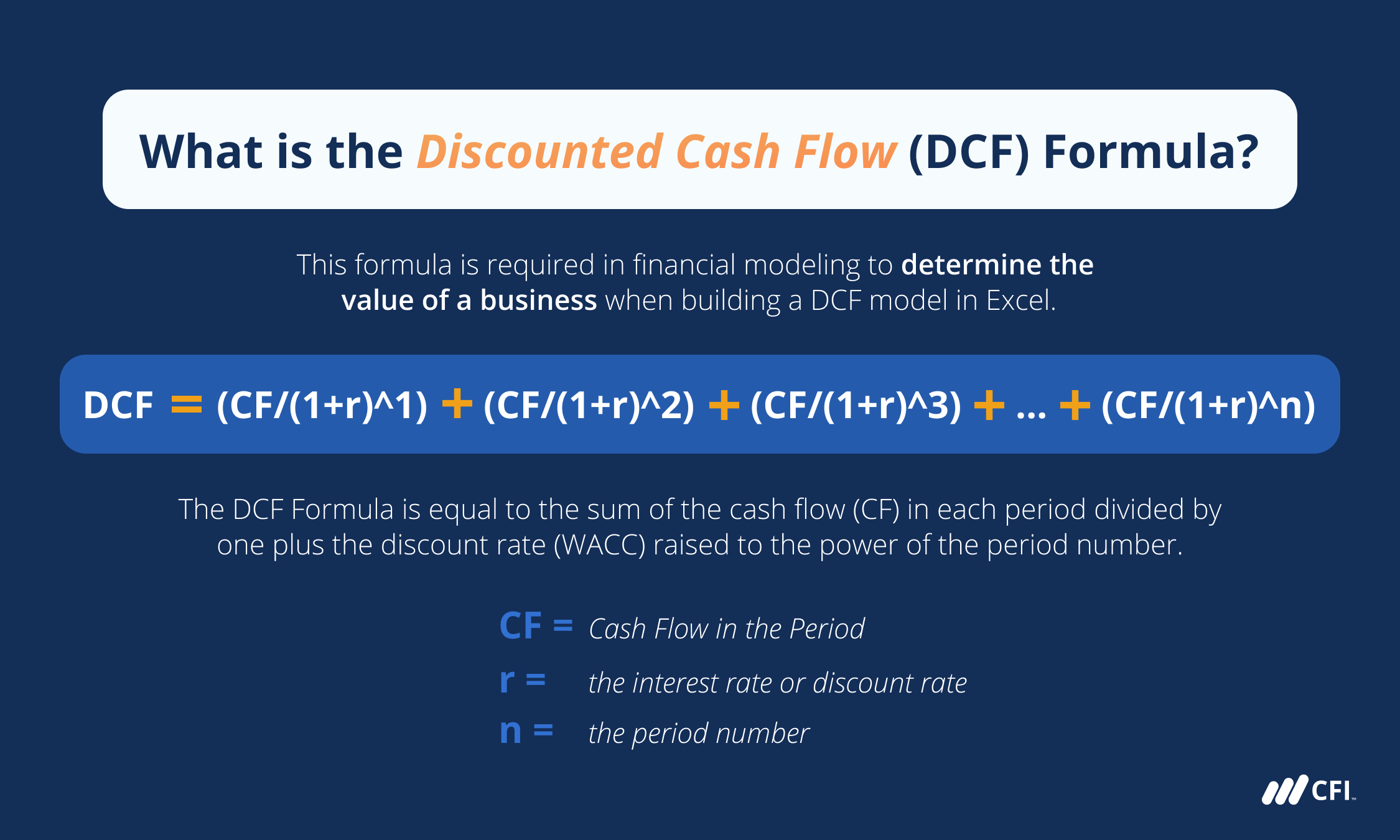
The discounted cash flow (DCF) model is a widely used valuation technique in finance and investing. It involves estimating the present value of future cash flows using a discount rate, which reflects the time value of money and the risk associated with those cash flows. Here, we’ll delve into the concept of a DCF table, its components, and how it’s used in valuation.
Understanding the DCF Model
The DCF model is based on the principle that the value of a company or an investment can be determined by the present value of its future cash flows. The key components of the DCF model include:
- Forecasted Cash Flows: These are the future cash inflows and outflows that an investor expects to receive from an investment. For companies, this often includes earnings, dividends, and free cash flows.
- Discount Rate: This is the rate at which the cash flows are discounted to their present value. It reflects the cost of capital and the risk-free rate, adjusted for the specific risk of the investment.
- Terminal Value: This represents the value of the investment beyond the forecast period, typically calculated using a perpetuity growth model or an exit multiple.
The DCF Table
A DCF table is a structured format used to organize and calculate the present value of future cash flows. The table typically includes the following columns:
- Year: The year in which the cash flow occurs.
- Cash Flow: The forecasted cash flow for each year.
- Discount Factor: The factor by which the cash flow is discounted to its present value, calculated as 1 / (1 + discount rate)^year.
- Present Value: The present value of the cash flow, calculated by multiplying the cash flow by the discount factor.
- Cumulative Present Value: The cumulative sum of the present values of the cash flows up to each year.
Example of a DCF Table
Let’s consider a simplified example of a company with forecasted free cash flows of 100, 120, 150, and 180 for the next four years, respectively. The discount rate is assumed to be 10%.
| Year | Cash Flow | Discount Factor | Present Value | Cumulative Present Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | $100 | 0.9091 | $90.91 | $90.91 |
| 2 | $120 | 0.8264 | $99.17 | $190.08 |
| 3 | $150 | 0.7513 | $112.70 | $302.78 |
| 4 | $180 | 0.6830 | $122.94 | $425.72 |
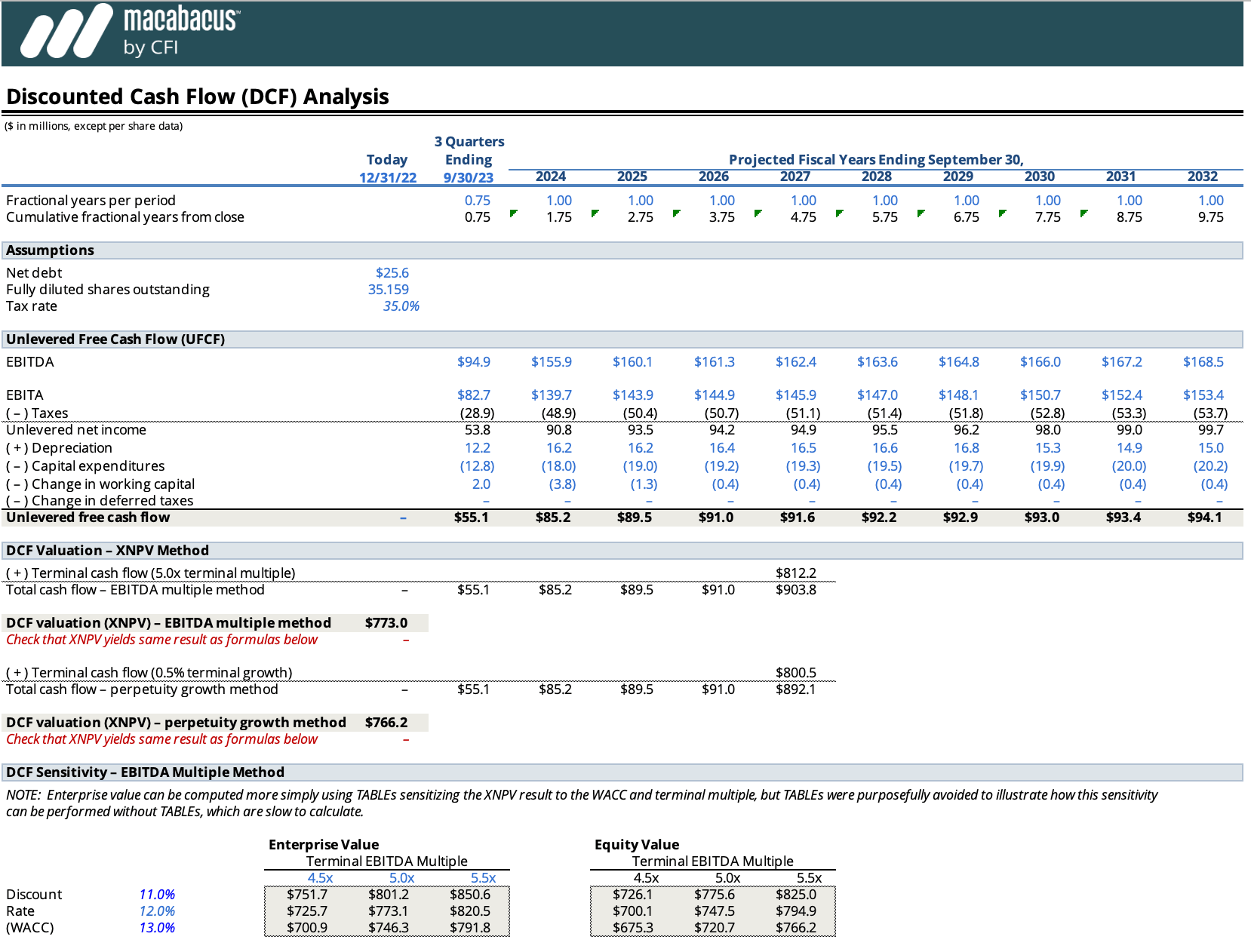
In this example, the present value of each year’s cash flow is calculated by multiplying the cash flow by the discount factor for that year. The cumulative present value shows the total present value of the cash flows up to each year, providing a clear picture of how the value of the investment grows over time.
Calculating Terminal Value
After the forecast period, the terminal value is often calculated to account for the value of the investment beyond the explicit forecast period. Two common methods for calculating terminal value are:
- Perpetuity Growth Model: Assumes that the cash flows will grow at a constant rate forever.
- Exit Multiple: Assumes the company will be sold at a certain multiple of its earnings or revenue at the end of the forecast period.
Conclusion
The DCF table is a powerful tool for valuing investments by providing a clear and structured approach to estimating the present value of future cash flows. By understanding the components of the DCF model and how to construct a DCF table, investors and analysts can make more informed decisions about the value of companies and investments.
FAQs
What is the purpose of the discount rate in a DCF analysis?
+The discount rate reflects the time value of money and the risk associated with the investment, allowing for the calculation of the present value of future cash flows.
How is the terminal value calculated in a DCF model?
+The terminal value can be calculated using either the perpetuity growth model, which assumes constant growth, or the exit multiple method, which assumes the company will be sold at a certain multiple of its earnings or revenue.
Why is the DCF model important in finance and investing?
+The DCF model provides a systematic approach to valuing investments based on their future cash flows, allowing investors to make informed decisions about the value of companies and investments.
In conclusion, understanding the DCF table and its components is essential for any investor or analyst looking to accurately value investments and make informed financial decisions. By applying the DCF model and considering the nuances of cash flow forecasting, discount rates, and terminal value, professionals can gain a deeper insight into the true value of investments.

