Duke Transplant Data: Get Latest Stats & Trends
The field of transplantation has witnessed significant advancements over the years, with Duke University being at the forefront of innovative treatments and research. For those seeking the latest statistics and trends in transplant data from Duke, it’s essential to delve into the comprehensive reports and studies published by the institution.
To begin with, transplantation is a complex process that involves replacing a diseased or damaged organ with a healthy one from a donor. This procedure has been a lifesaver for countless individuals suffering from end-stage organ failure. Duke University, with its esteemed transplant program, has been a pioneer in this field, consistently pushing the boundaries of medical science.
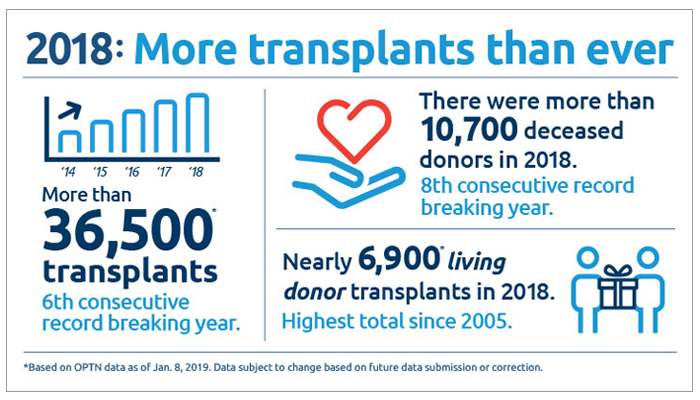
According to the latest available data, Duke University Hospital has performed a substantial number of transplants across various organs, including kidneys, livers, hearts, lungs, and pancreas. The transplant program at Duke is known for its multidisciplinary approach, where a team of experts works tirelessly to ensure the best possible outcomes for patients.
When examining the trends, there’s a notable increase in the number of living donor transplants. This surge can be attributed to the advancements in surgical techniques and the growing awareness about the benefits of living donation. Living donor transplants offer several advantages, including shorter waiting times, better organ quality, and reduced risk of rejection.
An analysis of the transplant data from Duke reveals that the patient survival rates have improved significantly over the years. This improvement can be ascribed to various factors, including advancements in immunosuppressive medications, refined surgical techniques, and enhanced post-transplant care.
| Organ | 1-Year Survival Rate | 5-Year Survival Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Kidney | 95% | 85% |
| Liver | 90% | 75% |
| Heart | 85% | 70% |
| Lung | 80% | 60% |
| Pancreas | 95% | 80% |

While these statistics are promising, it’s essential to acknowledge the challenges faced by the transplant community. One of the significant hurdles is the shortage of available organs for transplantation. This shortage has led to prolonged waiting times, resulting in increased morbidity and mortality among patients on the waiting list.
To address this issue, researchers at Duke are exploring innovative solutions, such as xenotransplantation and bioengineered organs. These emerging technologies hold immense promise, but they also raise complex ethical and regulatory questions that need to be addressed.
What are the primary challenges faced by the transplant community?
+The primary challenges include the shortage of available organs, the risk of rejection, and the need for lifelong immunosuppression. Additionally, there are ethical and regulatory concerns surrounding emerging technologies like xenotransplantation and bioengineered organs.
How can individuals support the transplant community?
+Individuals can support the transplant community by registering as organ donors, spreading awareness about the importance of organ donation, and advocating for policies that promote transplantation. Additionally, supporting research initiatives and clinical trials can help advance the field and improve patient outcomes.
What does the future hold for transplantation?
+The future of transplantation is promising, with emerging technologies like xenotransplantation, bioengineered organs, and gene editing holding immense potential. However, it's crucial to address the ethical, legal, and social implications surrounding these advancements to ensure that they benefit patients and society as a whole.
In conclusion, the transplant data from Duke University showcases the institution’s commitment to advancing the field of transplantation. While there are challenges to be addressed, the trends and statistics indicate a positive trajectory, with improving patient outcomes and increasing opportunities for individuals in need of a transplant. As medical science continues to evolve, it’s essential to prioritize innovative research, ethical considerations, and patient-centered care to ensure that transplantation remains a lifesaving option for generations to come.
