Electron Geometry H20
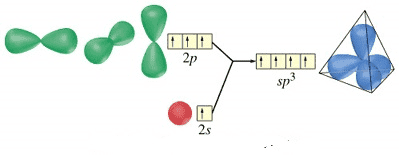
The electron geometry of H2O, also known as water, is a fundamental concept in chemistry that helps us understand the molecule’s shape and structure. To determine the electron geometry of H2O, we need to consider the number of electron groups around the central atom, which in this case is oxygen (O).
Oxygen has 6 valence electrons, and when it forms bonds with two hydrogen atoms, it shares 4 of these electrons in covalent bonds. This leaves 2 non-bonding electron pairs, also known as lone pairs, on the oxygen atom. The total number of electron groups around the oxygen atom is 4: 2 bonding pairs and 2 lone pairs.
Using the VSEPR (Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion) theory, we can predict the electron geometry of H2O. The VSEPR theory states that electron groups around a central atom will arrange themselves to minimize repulsions between them. In the case of H2O, the 4 electron groups around the oxygen atom will arrange themselves in a tetrahedral geometry, with the 2 lone pairs occupying 2 of the tetrahedral positions and the 2 bonding pairs occupying the other 2 positions.
However, when we consider the molecular geometry, which is the arrangement of atoms in space, the 2 lone pairs on the oxygen atom will occupy more space than the 2 bonding pairs, causing the bonding pairs to be pushed closer together. As a result, the molecular geometry of H2O is bent or V-shaped, with a bond angle of approximately 104.5°.
To further illustrate the electron geometry of H2O, let’s consider the following table:
| Electron Group | Type | Position |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Bonding pair | Tetrahedral position 1 |
| 2 | Bonding pair | Tetrahedral position 2 |
| 3 | Lone pair | Tetrahedral position 3 |
| 4 | Lone pair | Tetrahedral position 4 |

In this table, we can see that the 4 electron groups around the oxygen atom occupy tetrahedral positions, with the 2 lone pairs occupying 2 of the positions and the 2 bonding pairs occupying the other 2 positions.
It’s worth noting that the electron geometry of H2O is an important factor in determining its physical and chemical properties, such as its boiling point, melting point, and reactivity. Understanding the electron geometry of H2O is also crucial in understanding its role in various biological and chemical processes, such as protein folding and chemical reactions.
In addition to the VSEPR theory, there are other factors that can influence the electron geometry of H2O, such as the presence of other atoms or molecules that can interact with the oxygen atom. For example, in the presence of a strong acid, the oxygen atom in H2O can form a hydrogen bond with a hydrogen ion, which can affect the electron geometry of the molecule.
What is the molecular geometry of H2O?
+The molecular geometry of H2O is bent or V-shaped, with a bond angle of approximately 104.5°.
What is the VSEPR theory?
+The VSEPR theory states that electron groups around a central atom will arrange themselves to minimize repulsions between them.
Why is the electron geometry of H2O important?
+The electron geometry of H2O is important because it determines the physical and chemical properties of the molecule, such as its boiling point, melting point, and reactivity.
In conclusion, the electron geometry of H2O is a complex topic that requires a deep understanding of the VSEPR theory and the factors that influence the arrangement of electron groups around the central atom. By considering the number of electron groups and the repulsions between them, we can determine the electron geometry and molecular geometry of H2O, which is essential in understanding its physical and chemical properties.
Electron Geometry and Molecular Geometry Comparison
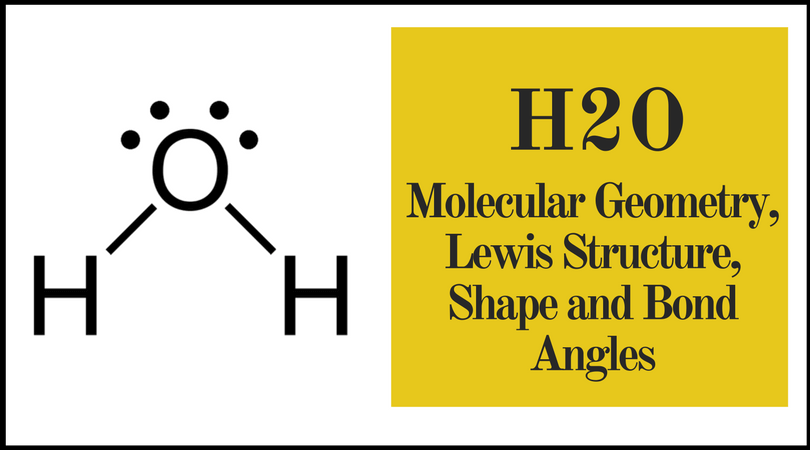
The following table compares the electron geometry and molecular geometry of H2O:
| Geometry | Description | Bond Angle |
|---|---|---|
| Electron Geometry | Tetrahedral | 109.5° |
| Molecular Geometry | Bent or V-shaped | 104.5° |
In this table, we can see that the electron geometry of H2O is tetrahedral, while the molecular geometry is bent or V-shaped. The bond angle of the electron geometry is approximately 109.5°, while the bond angle of the molecular geometry is approximately 104.5°.
Electron Geometry and Molecular Geometry Implications
The electron geometry and molecular geometry of H2O have important implications for its physical and chemical properties. For example, the bent or V-shaped molecular geometry of H2O allows it to form hydrogen bonds with other molecules, which is essential for its role in biological and chemical processes.
In addition, the electron geometry of H2O influences its reactivity, with the 2 lone pairs on the oxygen atom making it a good nucleophile. The molecular geometry of H2O also affects its boiling point and melting point, with the bent or V-shaped shape allowing it to form strong intermolecular forces with other molecules.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the electron geometry of H2O is a complex topic that requires a deep understanding of the VSEPR theory and the factors that influence the arrangement of electron groups around the central atom. By considering the number of electron groups and the repulsions between them, we can determine the electron geometry and molecular geometry of H2O, which is essential in understanding its physical and chemical properties. The electron geometry and molecular geometry of H2O have important implications for its role in biological and chemical processes, and understanding these concepts is crucial for advancing our knowledge of chemistry and biology.

