H2so4 Conjugate Base Explained
When exploring the realm of chemistry, particularly in the context of acids and bases, understanding the concept of conjugate bases is crucial. One of the most common and significant acids in chemistry is sulfuric acid, denoted by the chemical formula H2SO4. To grasp the concept of the conjugate base of H2SO4, we first need to delve into what sulfuric acid is and how it behaves in chemical reactions.
Introduction to Sulfuric Acid
Sulfuric acid is a strong mineral acid with the molecular formula H2SO4. It is a colorless, odorless, and syrupy liquid that is highly corrosive. In chemical reactions, sulfuric acid acts as a potent dehydrating agent and is widely used in various industrial processes, including the production of fertilizers, explosives, and pharmaceuticals. Due to its strong acidic properties, sulfuric acid readily donates a proton (H+ ion), making it a key player in acid-base reactions.
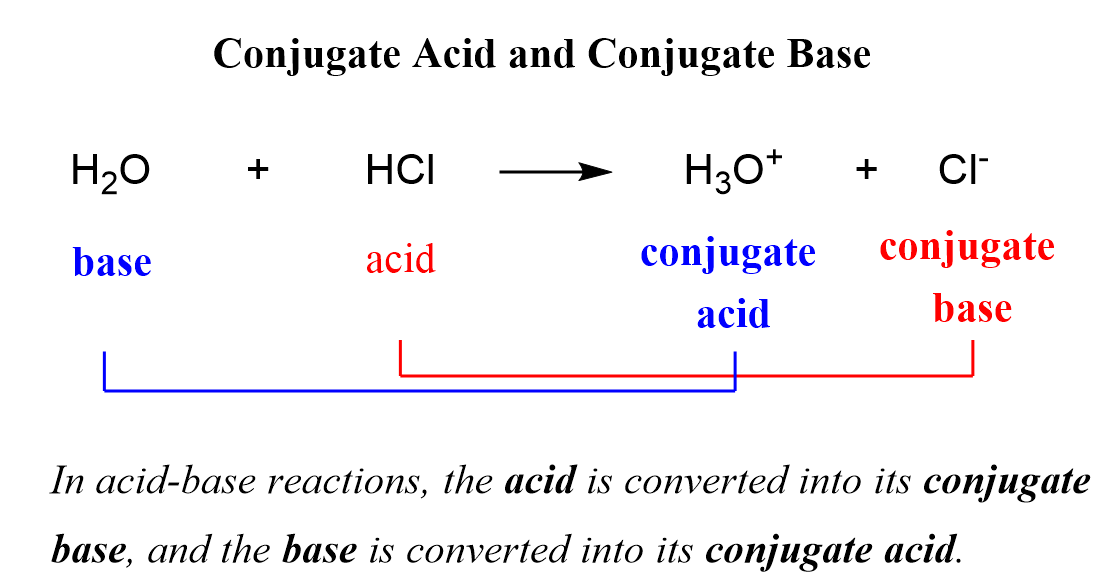
Understanding Conjugate Bases
In the context of acid-base chemistry, a conjugate base is what remains after an acid donates a proton (H+). The conjugate base of an acid is always a base because it can accept a proton to reform the original acid. This concept is fundamental to the Bronsted-Lowry theory of acids and bases, which defines an acid as a proton donor and a base as a proton acceptor.
The Conjugate Base of H2SO4
Given that sulfuric acid (H2SO4) is a diprotic acid, meaning it can donate two protons, its conjugate base can be considered in two steps:
- First Proton Donation: When H2SO4 donates its first proton (H+), it forms the bisulfate ion (HSO4-). The bisulfate ion acts as the conjugate base after the first proton donation.
H2SO4 → HSO4- + H+
- Second Proton Donation: If the bisulfate ion (HSO4-) donates another proton, it forms the sulfate ion (SO42-), which is the conjugate base after the second proton donation.
HSO4- → SO42- + H+
Thus, the conjugate bases of sulfuric acid are the bisulfate ion (HSO4-) after the first proton donation and the sulfate ion (SO42-) after the second proton donation. Both of these ions are bases because they can accept protons to revert to their respective acids.
Importance of Conjugate Bases in Chemistry
Understanding the conjugate bases of acids like sulfuric acid is vital for several reasons:
- Buffer Solutions: Conjugate bases can be used to create buffer solutions, which are crucial for maintaining a stable pH in various chemical and biological processes.
- Chemical Synthesis: The ability of conjugate bases to accept protons makes them essential reagents in organic synthesis, allowing for the formation of complex molecules.
- Environmental Science: The behavior of sulfuric acid and its conjugate bases is important in environmental science, particularly in understanding acid rain formation and its effects on ecosystems.
Practical Applications and Implications
The concept of conjugate bases has far-reaching implications in both industrial applications and natural processes:
- Industrial Processes: The controlled donation of protons by sulfuric acid and the subsequent formation of its conjugate bases are critical in numerous industrial processes, such as the production of detergents, dyes, and pharmaceuticals.
- Biological Systems: The balance between acids and their conjugate bases is crucial in biological systems, influencing enzyme activity, protein structure, and membrane transport.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the conjugate base of H2SO4, which can be either HSO4- or SO42- depending on the proton donation step, plays a pivotal role in understanding acid-base chemistry. The ability to donate and accept protons is fundamental to chemical reactions and has significant implications in industrial, environmental, and biological contexts. By grasping the concept of conjugate bases, we can better appreciate the complexities of chemical reactions and their applications in various fields.
FAQ Section
What is the conjugate base of a strong acid like H2SO4?
+The conjugate base of H2SO4 can be either HSO4- after the first proton donation or SO42- after the second proton donation, depending on the step of proton donation.
Why are conjugate bases important in chemistry?
+Conjugate bases are crucial for creating buffer solutions, acting as reagents in chemical synthesis, and understanding environmental and biological processes.
How does the concept of conjugate bases apply to real-world scenarios?
+The concept of conjugate bases has applications in industrial processes, environmental science, and biological systems, affecting the production of goods, ecosystem balance, and the functioning of living organisms.

