How Is Helium Used? Medical Benefits Guide
Helium, the second most abundant element in the universe, has been a subject of fascination for centuries. Beyond its common association with balloons and airships, helium has a multitude of uses that benefit various industries, including medicine. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the medical benefits of helium, exploring its applications, advantages, and the latest research in the field.
Historical Context: The Discovery of Helium’s Medical Properties
The use of helium in medicine dates back to the early 20th century, when it was first used as a breathing gas due to its non-reactive properties. The story of how helium was discovered to have medical benefits is as fascinating as it is crucial. In the 1930s, scientists began experimenting with helium as a potential treatment for respiratory diseases. They found that helium’s low density and non-irritating properties made it an ideal gas for therapeutic use.
Therapeutic Uses of Helium
Helium is used in various medical treatments, thanks to its unique properties. Some of the most notable therapeutic uses include:
- Respiratory Therapy: Helium-oxygen mixtures are used to treat respiratory conditions such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and pneumonia. The low density of helium reduces airway resistance, making it easier for patients to breathe.
- Diving Medicine: Helium is used in diving gas mixtures to reduce the risk of nitrogen narcosis and decompression sickness. Its low narcotic potential and rapid decompression characteristics make it an ideal choice for deep-sea diving.
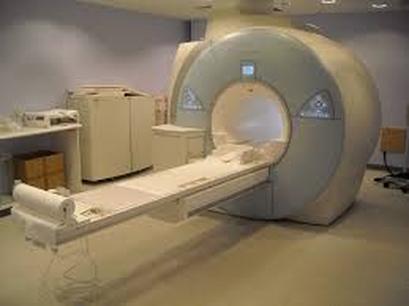
- Cryogenics: Liquid helium is used to cool superconducting materials, which are essential in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) machines. MRI technology relies on the superconducting properties of materials cooled by liquid helium to produce high-quality images of the body.
- Lung Function Testing: Helium is used in pulmonary function tests, such as helium dilution technique, to measure lung volume and capacity.
Medical Benefits of Helium
The medical benefits of helium are numerous and well-documented. Some of the most significant advantages include:
- Improved Breathing: Helium’s low density reduces airway resistance, making it easier for patients to breathe, especially in conditions such as asthma and COPD.
- Reduced Risk of Nitrogen Narcosis: Helium’s low narcotic potential makes it an ideal choice for deep-sea diving, reducing the risk of nitrogen narcosis and decompression sickness.
- High-Quality Imaging: The use of liquid helium in MRI machines enables the production of high-quality images, crucial for diagnosing and treating various medical conditions.
- Non-Invasive: Helium-based treatments are often non-invasive, reducing the risk of complications and promoting faster recovery times.
Future Directions: Emerging Research and Applications
As research continues to uncover the potential of helium in medicine, new applications and treatments are emerging. Some of the most promising areas of research include:
- Helium-Based Therapy for Neurological Disorders: Researchers are exploring the use of helium as a potential treatment for neurological disorders, such as multiple sclerosis and Parkinson’s disease.
- Helium-Enriched Air for Wound Healing: Studies have shown that helium-enriched air can enhance wound healing by increasing oxygen delivery to the affected area.
- Helium-Based Contrast Agents for Imaging: Scientists are developing helium-based contrast agents for use in MRI and other imaging modalities, which could improve image quality and diagnostic accuracy.
Practical Applications: A Step-by-Step Guide
For healthcare professionals and patients, understanding the practical applications of helium in medicine is crucial. Here is a step-by-step guide to using helium in respiratory therapy:
- Prepare the Helium-Oxygen Mixture: Mix helium and oxygen in the appropriate proportions, typically 70% helium and 30% oxygen.
- Administer the Mixture: Deliver the helium-oxygen mixture to the patient using a mask or ventilator.
- Monitor the Patient: Closely monitor the patient’s vital signs and adjust the mixture as needed.
Helium's unique properties make it an ideal gas for various medical applications. By understanding its uses, benefits, and future directions, healthcare professionals can harness the power of helium to improve patient outcomes and advance medical research.
Comparison of Helium with Other Gases
When compared to other gases, helium offers several advantages in medical applications. The following table summarizes the key differences:
| Gas | Density | Narcotic Potential | Use in Medicine |
|---|---|---|---|
| Helium | Low | Low | Respiratory therapy, diving medicine, cryogenics |
| Nitrogen | High | High | Not used in medical applications due to high narcotic potential |
| Oxygen | Medium | Low | Supplemental oxygen therapy, but not used alone due to risk of oxygen toxicity |

Addressing Potential Objections
Some may argue that the use of helium in medicine is limited due to its high cost and limited availability. However, advances in technology and production have made helium more accessible and affordable. Additionally, the benefits of helium in medical applications far outweigh the costs, making it a valuable investment in patient care.
Conclusion
In conclusion, helium’s medical benefits are vast and varied, from respiratory therapy to cryogenics and lung function testing. As research continues to uncover new applications and treatments, the use of helium in medicine is likely to expand. By understanding the unique properties and advantages of helium, healthcare professionals can harness its potential to improve patient outcomes and advance medical research.
What is the primary use of helium in medicine?
+The primary use of helium in medicine is as a breathing gas, due to its low density and non-irritating properties, making it ideal for treating respiratory conditions such as asthma and COPD.
How does helium improve breathing in patients with respiratory conditions?
+Helium’s low density reduces airway resistance, making it easier for patients to breathe, especially in conditions such as asthma and COPD.
What are the potential risks associated with using helium in medicine?
+The potential risks associated with using helium in medicine are limited, but may include gas embolism and oxygen toxicity. However, these risks can be mitigated with proper use and monitoring.


