How To Manage Hypoxia? Effective Care Plan Strategies
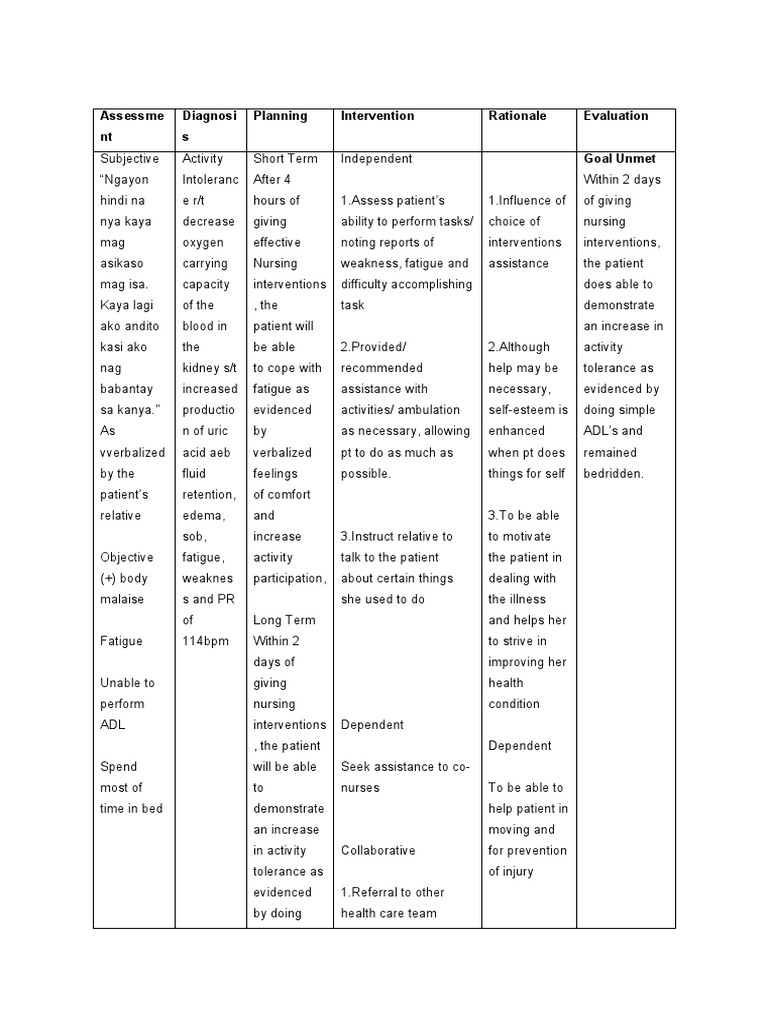
Hypoxia, a condition characterized by insufficient oxygen supply to tissues and organs, can have severe consequences if not managed properly. Effective care plan strategies are crucial to prevent complications, improve patient outcomes, and enhance quality of life. In this article, we will delve into the complexities of hypoxia, explore its causes and consequences, and provide comprehensive guidance on managing this condition.
Understanding Hypoxia
Hypoxia occurs when the body, or a region of the body, is deprived of adequate oxygen supply. This can be due to various factors, including high altitude, anemia, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), pneumonia, or cardiac conditions. The severity of hypoxia can vary, ranging from mild to severe, and its management depends on the underlying cause, severity, and individual patient needs.
Assessing Oxygen Levels
Accurate assessment of oxygen levels is critical in managing hypoxia. This can be achieved through:
- Pulse Oximetry: A non-invasive method using a pulse oximeter to measure oxygen saturation (SpO2) in the blood.
- Arterial Blood Gas (ABG) Analysis: An invasive test that provides detailed information about oxygen levels, carbon dioxide levels, and pH balance in the blood.
Care Plan Strategies for Hypoxia Management
Effective management of hypoxia involves a multi-faceted approach that includes:
1. Oxygen Therapy
Oxygen therapy is the primary treatment for hypoxia, aimed at increasing oxygen levels in the blood. This can be administered through various devices, including nasal cannulas, face masks, or ventilators, depending on the severity of the condition and patient requirements.
2. Addressing Underlying Causes
Treating the underlying cause of hypoxia is crucial. For example, if hypoxia is due to COPD, management strategies might include medications to improve lung function, pulmonary rehabilitation, and smoking cessation programs.
3. Lifestyle Modifications
Patients with hypoxia can benefit from lifestyle modifications, such as: - Physical Activity: Gentle exercises, as prescribed by healthcare professionals, can improve oxygen utilization and overall health. - Nutritional Advice: A balanced diet rich in iron, vitamins, and minerals can help improve oxygen delivery and utilization. - Smoking Cessation: Quitting smoking is essential for patients with respiratory conditions leading to hypoxia.
4. Monitoring and Follow-Up
Regular monitoring of oxygen levels and follow-up appointments with healthcare providers are vital. This allows for timely adjustments to the care plan, management of potential complications, and optimization of treatment strategies.
Advanced Therapeutic Options
In severe cases of hypoxia, or when conventional treatments are insufficient, advanced therapeutic options may be considered:
- Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy: Involves breathing pure oxygen in a pressurized room or chamber, which can enhance oxygen delivery to tissues.
- Mechanical Ventilation: May be necessary for patients with severe respiratory failure, providing supportive care until the underlying condition improves.
Patient Education and Support
Educating patients and their families about hypoxia, its management, and the importance of adherence to the care plan is crucial. This includes understanding the condition, recognizing signs of worsening hypoxia, and knowing when to seek emergency care.
Conclusion
Managing hypoxia effectively requires a comprehensive and personalized approach. By understanding the causes, assessing oxygen levels accurately, and implementing appropriate care plan strategies, healthcare providers can improve patient outcomes, reduce complications, and enhance the quality of life for individuals affected by this condition.
What are the common causes of hypoxia?
+Hypoxia can be caused by various factors, including high altitude, anemia, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), pneumonia, and cardiac conditions. Understanding the underlying cause is crucial for effective management.
How is oxygen therapy administered?
+Oxygen therapy can be administered through nasal cannulas, face masks, or ventilators, depending on the severity of the condition and patient requirements. The choice of device is tailored to the individual's needs and the underlying cause of hypoxia.
What lifestyle modifications can help manage hypoxia?
+Lifestyle modifications such as gentle physical activity, a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients, and smoking cessation can significantly contribute to the management of hypoxia. These changes can improve oxygen utilization, reduce symptoms, and enhance overall health.
By adopting a holistic approach to hypoxia management, incorporating both medical treatments and lifestyle adjustments, individuals can better cope with this condition and improve their overall well-being. Continuous monitoring and follow-up care are essential components of an effective care plan, ensuring that treatment strategies are optimized and adapted as needed to address the evolving needs of the patient.