Identify Oak By Leaf
To accurately identify an oak tree by its leaf, it’s essential to understand the characteristics that distinguish oak leaves from those of other tree species. Oak trees belong to the genus Quercus, with over 600 species worldwide, each having unique leaf features. However, there are some common traits among oak leaves that can help in identification.
General Characteristics of Oak Leaves
- Lobes and Sinuses: Many oak leaves are known for their lobed or deeply toothed margins. The lobes are the pointed parts of the leaf, and the sinuses are the spaces between these lobes. Some oaks have shallow lobes, while others have deep ones.
- Leaf Shape and Size: Oak leaves vary greatly in shape and size, depending on the species. They can be elliptical, ovate, or lance-shaped and range from a few inches to over a foot in length.
- Leaf Venation: Oak leaves typically have a network of veins that can be hairy or smooth, depending on the species.
- Color and Texture: The upper surface of oak leaves is usually a dark green, while the underside can be lighter green or even hairy in some species. The texture of the leaf can be smooth, hairy, or have a waxy feel.
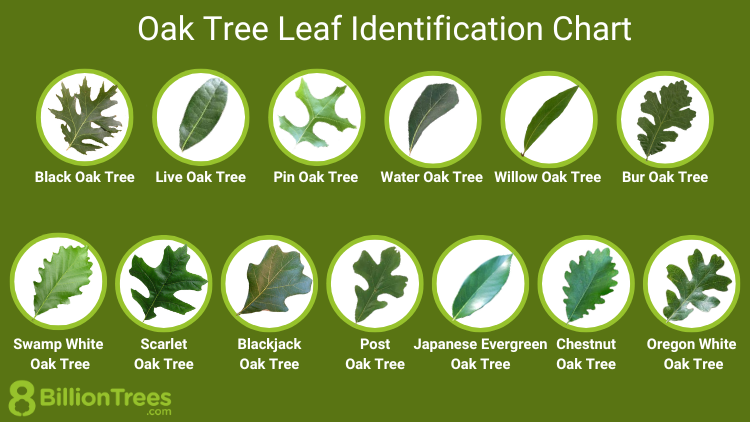
Common Types of Oak Leaves
- White Oak Leaves: These typically have rounded lobes and are often found on trees like the White Oak (Quercus alba) and the English Oak (Quercus robur).
- Red Oak Leaves: Characterized by pointed lobes, these are seen on trees such as the Northern Red Oak (Quercus rubra) and the Scarlet Oak (Quercus coccinea).
- Live Oak Leaves: Usually elliptical and without deep lobes, these are found on species like the Southern Live Oak (Quercus virginiana).
Steps for Identification
- Observe the Shape: Start by looking at the overall shape of the leaf. Is it broad and rounded, or is it more narrow and pointed?
- Count the Lobes: If the leaf has lobes, count them. Different oak species have different numbers of lobes.
- Check the Sinuses: Look at the depth and shape of the sinuses (the spaces between the lobes). Deep sinuses often indicate a red oak, while shallow sinuses might suggest a white oak.
- Examine the Margins: Are the edges of the leaf smooth, toothed, or deeply lobed?
- Consider the Size: Measure the length and width of the leaf. Knowing the size can help narrow down the species.
- Look at the Leaf Stem (Petiole): The length and color of the petiole can also be clues. Some oaks have very short petioles, while others have longer ones.
- Consult a Field Guide or Expert: For precise identification, especially among similar species, consulting a detailed field guide or an expert in botany can be invaluable.
Preservation and Further Study
If you’re interested in studying the leaf further or preserving it for later identification, pressing the leaf between sheets of paper or using a plant press can help flatten it, making it easier to examine its features. Digital photography can also be useful for documenting the leaf and comparing it with pictures in field guides or online databases.
Identifying oak trees by their leaves requires patience and attention to detail, but with practice, you can become proficient in recognizing the various species and their unique characteristics. Remember, each species of oak has its distinctive features, so taking a close and careful look is key to accurate identification.
What are the primary characteristics to look for when identifying an oak tree by its leaf?
+The primary characteristics include the shape and depth of the lobes, the color and texture of the leaf, the pattern of the venation, and the length and characteristics of the leaf stem (petiole).
How do the leaves of white oak and red oak trees differ?
+White oak leaves typically have rounded lobes and shallow sinuses, while red oak leaves have pointed lobes and deeper sinuses. This distinction is a key factor in differentiating between the two main categories of oak trees.
What tools or resources are most helpful for the precise identification of oak tree species?
+Detailed field guides, botanical manuals, and consultations with experts in botany or forestry are invaluable resources. Additionally, using digital tools and databases that offer high-quality images and descriptions of various oak species can aid in accurate identification.
Whether you’re a seasoned naturalist or just beginning to explore the world of botany, the unique characteristics of oak leaves offer a fascinating area of study. By combining observation skills with the right resources, anyone can deepen their understanding and appreciation of these magnificent trees.