Map Of Mexican Border
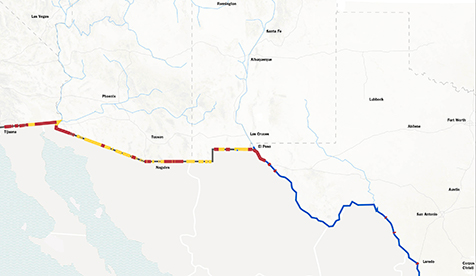
The Mexican border, formally known as the Mexico–United States border, stretches for approximately 1,954 miles (3,145 kilometers) from the Pacific Ocean to the Gulf of Mexico. It separates the United States from Mexico, dividing the two countries and marking the beginning of their distinct territories. This extensive boundary is not just a physical line but also a cultural, economic, and political divide that has played a significant role in the history and development of both nations.
To better understand the layout and significance of the Mexican border, it’s essential to visualize its geography and key points of interest. The border begins at the Pacific Ocean, where the Mexican state of Baja California meets the U.S. state of California. From there, it extends southeast, passing through various terrains, including deserts, mountains, and rivers, and ends at the Gulf of Mexico, where the Mexican state of Tamaulipas meets the U.S. state of Texas.
Some of the notable geographical features along the Mexican border include the Rio Grande, which forms a significant portion of the border between the U.S. and Mexico, especially in the eastern part of the border. The Sonoran Desert, one of the largest and hottest deserts in North America, covers a substantial area of the border region, particularly in Arizona and the Mexican state of Sonora. The desert’s harsh conditions have made it a challenging and dangerous area for those attempting to cross the border.
Segments of the Mexican Border

The Mexican border can be divided into several segments, each with its unique characteristics and challenges:
California Border: This segment begins at the Pacific Ocean and extends eastward, passing through the California desert and the mountains of California and Baja California. The cities of San Diego, California, and Tijuana, Baja California, are major urban centers along this part of the border.
Arizona Border: The Arizona segment of the border is predominantly desert, with the Sonoran Desert covering a large area. This region is known for its extreme heat and lack of water sources, making it particularly hazardous for migrants. The cities of Nogales, Arizona, and Nogales, Sonora, are significant border crossing points.
New Mexico Border: This segment is relatively short, with the Rio Grande forming a natural barrier between New Mexico and the Mexican state of Chihuahua. The cities of Albuquerque, New Mexico, and Ciudad Juárez, Chihuahua, are major urban areas, with Ciudad Juárez being a significant crossing point.
Texas Border: The Texas segment is the longest part of the U.S.-Mexico border, stretching from El Paso to the Gulf of Mexico. The Rio Grande runs along most of this segment, passing through various landscapes, including deserts and fertile river valleys. Major cities along this part of the border include El Paso, Texas, and Ciudad Juárez, Chihuahua, in the west, and Brownsville, Texas, and Matamoros, Tamaulipas, in the east.
What are the main challenges faced by those crossing the Mexican border?
+Those attempting to cross the Mexican border face numerous challenges, including extreme weather conditions, lack of access to water and food, risk of deportation, and potential violence from criminal organizations. The harsh desert environment, particularly in the Arizona segment, poses significant dangers, including dehydration and heat stroke.
How does the geography of the Mexican border influence migration patterns?
+The geography of the Mexican border plays a crucial role in shaping migration patterns. The natural barriers, such as the Rio Grande and the Sonoran Desert, force migrants to choose specific crossing points, which can be more dangerous and challenging. Additionally, the mountainous regions and deserts pose significant obstacles, leading many to attempt crossings at more urbanized areas or through official ports of entry.
Economic and Cultural Significance

The Mexican border is not just a physical divide; it also represents a significant economic and cultural boundary. The region is home to numerous border cities, which have developed unique cultural identities shaped by the intersection of American and Mexican influences. These cities, such as San Diego-Tijuana and El Paso-Ciudad Juárez, have become crucial economic hubs, with trade, tourism, and manufacturing being major contributors to their economies.
Furthermore, the border region is rich in cultural heritage, with a blend of indigenous, Spanish, and American influences. The cuisine, music, and art of the region reflect this diversity, making it a vibrant and dynamic area that attracts visitors from all over the world.
In conclusion, the Mexican border is a complex and multifaceted entity that extends beyond its physical boundaries. It is a region of rich cultural heritage, significant economic importance, and challenging geographical conditions. Understanding the map of the Mexican border and its various segments can provide valuable insights into the history, present, and future of this critical international boundary.
Understanding the Complexity of the Mexican Border
- Geographical Diversity: Recognize the varied landscapes along the border, from deserts to rivers and mountains, and how these impact migration and daily life.
- Cultural Significance: Appreciate the unique cultural identities of border cities and the blending of American and Mexican influences.
- Economic Importance: Understand the role of trade, tourism, and manufacturing in the border region's economy and its impact on both the U.S. and Mexico.
- Challenges and Opportunities: Acknowledge the challenges faced by those crossing the border, including environmental hazards and legal barriers, while also recognizing the opportunities for cultural exchange and economic cooperation.
By embracing a nuanced understanding of the Mexican border, individuals can foster a deeper appreciation for the complexities and opportunities that this international boundary presents. Whether viewed through the lens of geography, culture, economy, or policy, the Mexican border stands as a significant and multifaceted entity that continues to shape the lives of millions of people in the United States, Mexico, and beyond.