Picture Of A Blood Clot
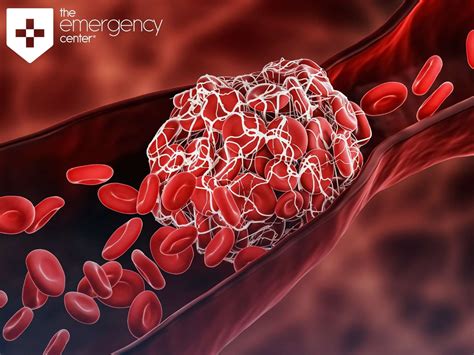
The formation of a blood clot is a complex process that involves multiple cellular and molecular components. A blood clot, also known as a thrombus, is a gel-like mass that forms when blood coagulates. It is composed of a mixture of blood cells, platelets, and fibrin, a protein that acts as a glue to hold the clot together.
Structure of a Blood Clot
A blood clot has a distinct structure, which can be broken down into several layers. The innermost layer, known as the nucleus, is composed of platelets and fibrin. This layer is surrounded by a layer of erythrocytes, or red blood cells, which are trapped in the clot. The outermost layer, known as the capsule, is composed of a thin layer of fibrin and platelets.
Types of Blood Clots
There are several types of blood clots, each with distinct characteristics. Some common types include:
- Arterial thrombus: A blood clot that forms in an artery, which can lead to a heart attack or stroke.
- Venous thrombus: A blood clot that forms in a vein, which can lead to deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or pulmonary embolism (PE).
- Microthrombus: A small blood clot that forms in the microcirculation, which can lead to tissue damage and organ dysfunction.
Formation of a Blood Clot
The formation of a blood clot is a complex process that involves multiple cellular and molecular components. The process can be broken down into several steps:
- Vascular injury: The formation of a blood clot is often triggered by vascular injury, such as a cut or a bruise.
- Platelet activation: Platelets are activated and aggregate at the site of injury, forming a platelet plug.
- Coagulation cascade: The coagulation cascade is activated, leading to the formation of fibrin and the strengthening of the clot.
- Clot retraction: The clot is retracted, which involves the contraction of platelets and the formation of a more solid clot.
Dissolution of a Blood Clot
The dissolution of a blood clot is a natural process that involves the breakdown of the clot by the body’s own enzymes. This process is known as fibrinolysis. The breakdown of the clot is mediated by the enzyme plasmin, which breaks down the fibrin component of the clot.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a blood clot is a complex structure that plays a crucial role in the body’s response to injury. Understanding the structure, types, and formation of blood clots is essential for the diagnosis and treatment of thrombotic disorders.
What is the main component of a blood clot?
+The main component of a blood clot is fibrin, a protein that acts as a glue to hold the clot together.
What is the difference between an arterial thrombus and a venous thrombus?
+An arterial thrombus forms in an artery, while a venous thrombus forms in a vein. Arterial thrombi are more likely to lead to heart attack or stroke, while venous thrombi are more likely to lead to deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism.
How is a blood clot dissolved?
+A blood clot is dissolved through the process of fibrinolysis, which involves the breakdown of the clot by the body's own enzymes, including plasmin.
The formation and dissolution of blood clots are complex processes that involve multiple cellular and molecular components. Understanding these processes is essential for the diagnosis and treatment of thrombotic disorders.
Steps to Prevent Blood Clots
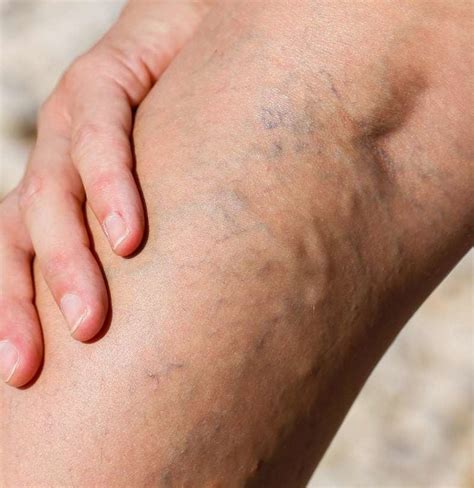
- Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water
- Exercise regularly to improve circulation
- Avoid prolonged periods of immobility
- Manage chronic conditions, such as high blood pressure and diabetes
- Consider taking anticoagulant medication if recommended by a doctor
Advantages and Disadvantages of Anticoagulant Medication

| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Reduces the risk of blood clots | Increases the risk of bleeding |
| Can be effective in preventing stroke and heart attack | Can interact with other medications |
| Can be used to treat deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism | Requires regular monitoring of blood tests |


