State Ranking In Education
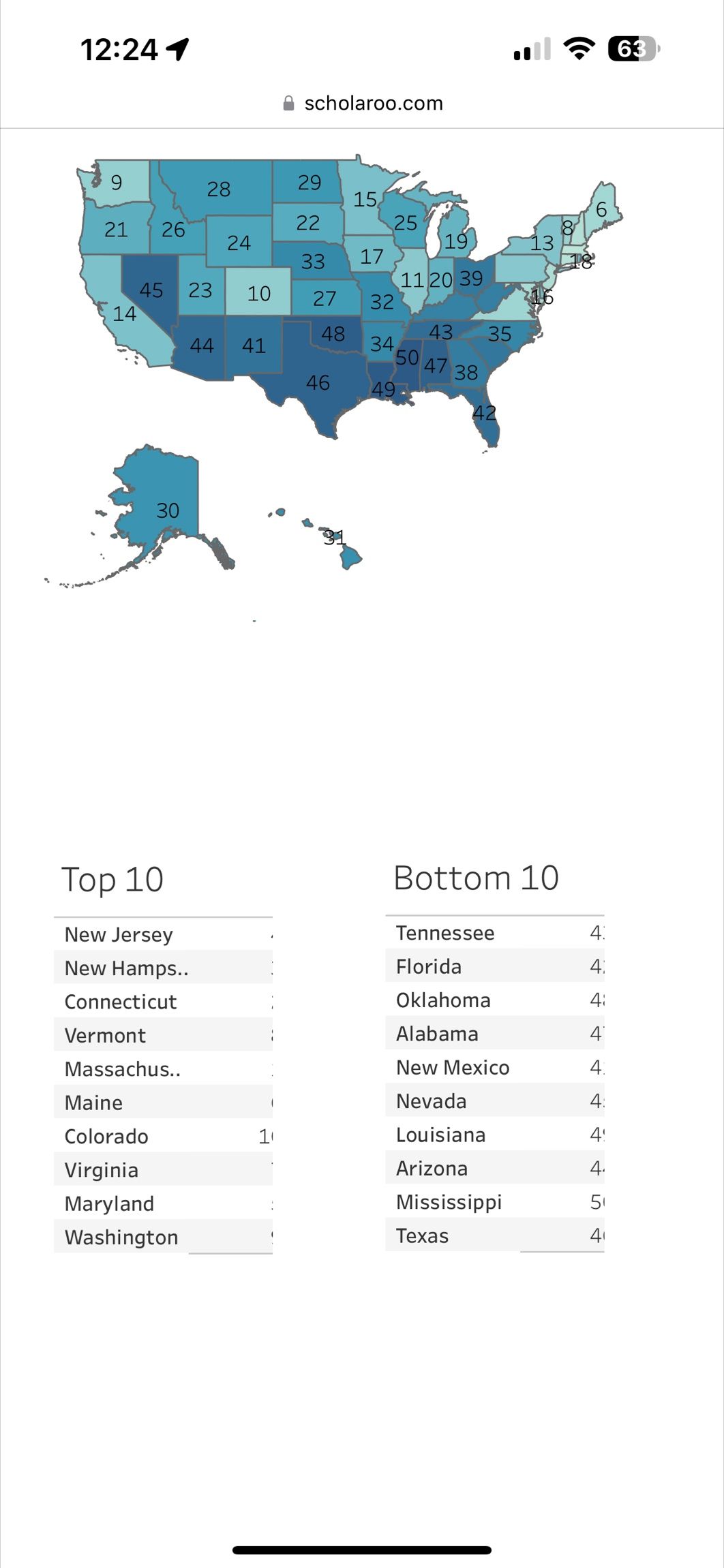
The performance of states in education is a crucial aspect of understanding the overall quality and effectiveness of educational systems across different regions. Educational rankings can provide valuable insights into how states compare in terms of academic achievement, educational attainment, and the overall educational environment. These comparisons can help identify areas of strength and weakness, guiding policy decisions and resource allocation to improve educational outcomes.
One of the key challenges in ranking states by their educational performance is determining the most relevant and meaningful criteria. Common metrics include high school graduation rates, average scores on standardized tests such as the SAT or ACT, the percentage of the population holding a bachelor’s degree or higher, and funding per student. Each of these metrics provides a different lens through which to view educational performance, highlighting the complexity of assessing educational quality.
Factors Influencing Educational Rankings
Several factors influence a state’s ranking in education, including but not limited to:
Funding: The amount of money allocated to education can significantly impact the quality of educational services. States with higher spending per student often have better resources, lower student-to-teacher ratios, and can attract higher-quality teachers.
Demographic Factors: The socioeconomic status of the student population, family stability, and access to early childhood education are critical. States with more disadvantaged populations may face additional challenges in achieving high educational outcomes.
Policy and Governance: Educational policies, such as those related to teacher certification, curriculum standards, and school choice, can affect educational quality. Effective governance and leadership at both the state and local levels are essential for implementing policies that support educational excellence.
Innovation and Technology Integration: The incorporation of technology and innovative teaching methods can enhance learning outcomes. States that invest in educational technology and support innovative educational practices may see improved performance.
Methodology for Ranking
Ranking states by their educational performance involves collecting and analyzing data on various educational indicators. This can include:
- High School Graduation Rates: The percentage of students who graduate from high school within four years.
- College Readiness: Often measured by scores on the SAT or ACT, this indicates how well high school graduates are prepared for college-level work.
- Educational Attainment: The percentage of the population with a high school diploma, bachelor’s degree, or higher.
- Student-Teacher Ratio: A lower ratio can indicate more personalized attention for students.
- Spending per Student: The amount of money spent on each student’s education, which can affect the quality of resources and instruction.
Challenges and Considerations
While rankings can provide a snapshot of educational performance, they also have limitations. For instance, they may not fully capture the quality of education or the challenges faced by different states. Additionally, overreliance on standardized test scores can lead to teaching practices that prioritize test preparation over deeper learning and critical thinking skills.
Conclusion
Ranking states by their education performance is a complex task that involves analyzing multiple factors and metrics. While such rankings can offer insights into the strengths and weaknesses of educational systems across different states, they must be interpreted with caution, recognizing both their utility and their limitations. Ultimately, the goal of educational assessment should be to identify areas for improvement and to inform strategies that enhance educational outcomes for all students, regardless of their geographical location.
FAQs
What factors are most commonly used to rank states by their educational performance?
+Common factors include high school graduation rates, average scores on standardized tests, educational attainment levels, and spending per student.
Why is funding an important consideration in state educational rankings?
+Funding can impact the quality of educational services, including the ability to attract and retain high-quality teachers, maintain lower student-to-teacher ratios, and provide access to advanced educational resources and technology.
What are some limitations of using rankings to assess educational performance?
+Rankings may not fully capture the quality of education or account for the socio-economic challenges faced by different states. Overreliance on certain metrics, like standardized test scores, can also lead to narrowed curriculum focus and teaching practices that prioritize test preparation over broader educational goals.

