Thyroid Gland Size: Ultrasound Measurement Mastery
The thyroid gland, a butterfly-shaped endocrine gland located in the neck, plays a crucial role in regulating metabolism, growth, and development. Accurate measurement of thyroid gland size is essential for diagnosing and managing various thyroid disorders, such as hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, and thyroid nodules. Ultrasound technology has become the gold standard for assessing thyroid gland size due to its non-invasive, cost-effective, and highly accurate nature.
Understanding Thyroid Gland Anatomy
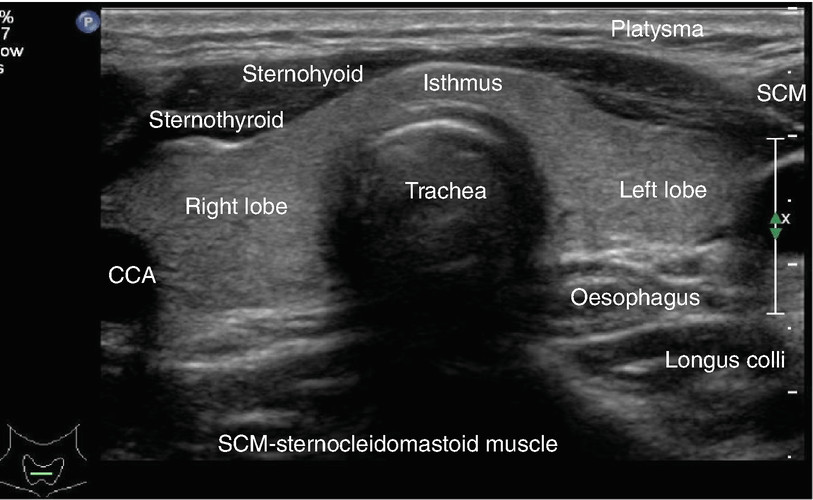
Before delving into the ultrasound measurement of thyroid gland size, it’s essential to understand the anatomy of the thyroid gland. The thyroid gland consists of two lobes, connected by an isthmus, which lies anterior to the trachea. The right lobe is typically larger than the left lobe, and the gland is surrounded by a thin layer of connective tissue. The thyroid gland is also closely related to other vital structures, such as the parathyroid glands, trachea, and esophagus.
Ultrasound Measurement Techniques
Ultrasound measurement of thyroid gland size involves using a high-frequency transducer (typically 7.5-12 MHz) to produce high-resolution images of the gland. There are several ultrasound measurement techniques used to assess thyroid gland size, including:
- Longitudinal measurement: Measuring the length of the thyroid lobe from the superior to the inferior pole.
- Transverse measurement: Measuring the width of the thyroid lobe from the medial to the lateral border.
- Anteroposterior measurement: Measuring the depth of the thyroid lobe from the anterior to the posterior border.
- Volume calculation: Calculating the volume of the thyroid lobe using the formula: length x width x depth x 0.5.
Normal Thyroid Gland Size
The normal thyroid gland size varies depending on age, sex, and body size. Generally, the normal thyroid gland size is:
- Length: 4-6 cm (1.6-2.4 in)
- Width: 1.3-1.8 cm (0.5-0.7 in)
- Depth: 1-2 cm (0.4-0.8 in)
- Volume: 10-20 mL (0.34-0.68 oz)
Thyroid Gland Size in Different Conditions
Thyroid gland size can vary significantly in different conditions, such as:
- Hypothyroidism: The thyroid gland may be smaller than normal, with a reduced volume.
- Hyperthyroidism: The thyroid gland may be larger than normal, with an increased volume.
- Thyroid nodules: The presence of thyroid nodules can cause the thyroid gland to become irregularly shaped and enlarged.
- Thyroid cancer: The thyroid gland may be larger than normal, with a irregular shape and ultrasound characteristics suggestive of malignancy.
Clinical Significance of Thyroid Gland Size
Accurate measurement of thyroid gland size has significant clinical implications, including:
- Diagnosis: Ultrasound measurement of thyroid gland size can help diagnose various thyroid disorders, such as hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, and thyroid nodules.
- Treatment planning: Thyroid gland size can influence treatment planning, such as the dose of radioactive iodine for hyperthyroidism or the need for surgical intervention for thyroid cancer.
- Monitoring disease progression: Serial ultrasound measurements of thyroid gland size can help monitor disease progression and response to treatment.
Common Challenges and Limitations
Despite the advantages of ultrasound measurement of thyroid gland size, there are several challenges and limitations to consider, including:
- Operator dependence: Ultrasound measurement of thyroid gland size can be operator-dependent, requiring skilled and experienced sonographers.
- Variability in measurement: There can be variability in measurement due to differences in ultrasound equipment, measurement techniques, and patient positioning.
- Difficulty in measuring nodular glands: Measuring thyroid gland size can be challenging in patients with nodular glands, as the nodules can distort the normal anatomy of the gland.
Future Directions and Emerging Trends
The field of thyroid ultrasound is continuously evolving, with emerging trends and technologies, such as:
- Artificial intelligence: The use of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to improve the accuracy and efficiency of thyroid ultrasound measurements.
- 3D ultrasound: The development of 3D ultrasound technology to provide more accurate and detailed measurements of thyroid gland size.
- Contrast-enhanced ultrasound: The use of contrast agents to improve the visualization of thyroid nodules and lesions.
What is the normal size of the thyroid gland?
+The normal thyroid gland size varies depending on age, sex, and body size, but generally, the normal thyroid gland size is: length: 4-6 cm, width: 1.3-1.8 cm, depth: 1-2 cm, and volume: 10-20 mL.
What are the common indications for thyroid ultrasound?
+Common indications for thyroid ultrasound include: evaluation of thyroid nodules, assessment of thyroid gland size and morphology, diagnosis of thyroid disorders, such as hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism, and monitoring of disease progression and response to treatment.
What are the advantages of ultrasound measurement of thyroid gland size?
+The advantages of ultrasound measurement of thyroid gland size include: non-invasive, cost-effective, highly accurate, and ability to provide detailed information about thyroid gland morphology and function.
In conclusion, accurate measurement of thyroid gland size using ultrasound technology is essential for diagnosing and managing various thyroid disorders. While there are challenges and limitations to consider, the advantages of ultrasound measurement of thyroid gland size make it an invaluable tool in the field of thyroidology. As the field continues to evolve, emerging trends and technologies, such as artificial intelligence, 3D ultrasound, and contrast-enhanced ultrasound, will likely improve the accuracy and efficiency of thyroid ultrasound measurements.
