Thyroid Normal Size Ultrasound
When it comes to assessing the health of the thyroid gland, ultrasound technology plays a crucial role. The ultrasound examination provides valuable information about the size, structure, and functionality of the thyroid, helping doctors diagnose and manage thyroid-related disorders. A key aspect of thyroid health is its size, as both enlargement (goiter) and shrinkage can be indicative of underlying issues. In this context, understanding what constitutes a normal thyroid size on an ultrasound is essential for accurate diagnoses and appropriate treatment plans.
Normal Thyroid Size Range
The thyroid gland is located in the neck, below the Adam’s apple, and consists of two lobes connected by an isthmus. The size of the thyroid can vary among individuals due to factors such as age, sex, and iodine intake. Generally, a normal thyroid lobe is approximately 2 cm in length and about 1.3 to 1.5 cm in width and depth. However, these dimensions can slightly vary, and what is considered “normal” can depend on the specific criteria used by different medical institutions.
Factors Influencing Thyroid Size
Several factors can influence thyroid size, making it essential to consider these variables when interpreting ultrasound results:
- Iodine Intake: Iodine deficiency is a common cause of thyroid enlargement (goiter) worldwide. Areas with low iodine intake in the diet may have higher prevalence rates of goiter.
- Age and Sex: Thyroid size can change with age and may also differ between sexes. For example, thyroid size tends to increase with age, and women are more likely to have larger thyroids than men.
- Pregnancy: During pregnancy, the thyroid may become slightly larger due to increased levels of estrogen, which can stimulate thyroid growth.
- Thyroid Diseases: Conditions such as hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) or hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid) can affect thyroid size. For instance, Graves’ disease, a cause of hyperthyroidism, can lead to thyroid enlargement.
Ultrasound Evaluation of Thyroid Size
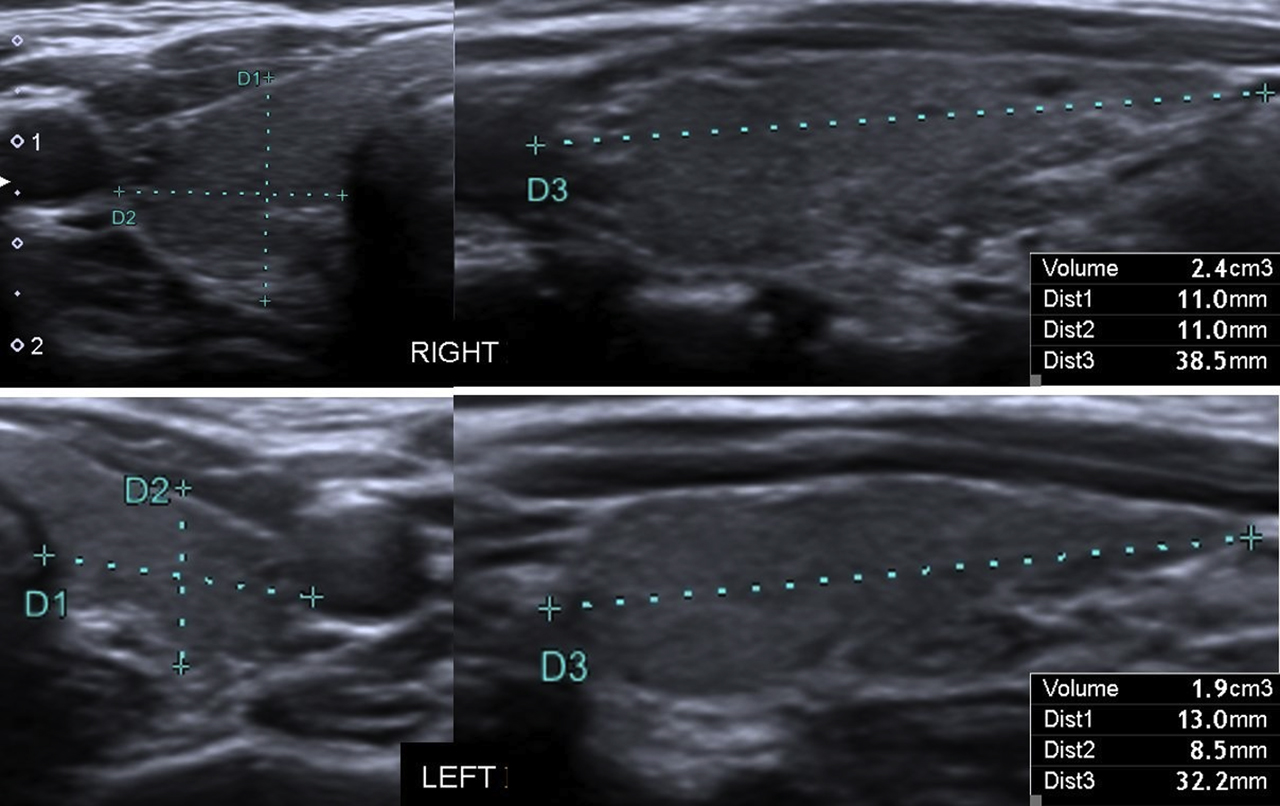
Ultrasound is the preferred method for evaluating thyroid size and structure due to its non-invasive nature, lack of radiation exposure, and high sensitivity for detecting thyroid nodules and other abnormalities. During an ultrasound, a healthcare professional will place a gel on the neck area and use a probe to capture images of the thyroid gland. The size of each thyroid lobe is measured in three dimensions (length, width, and depth), and the volume is calculated using a formula.
Volume Calculation
The volume of the thyroid lobe is calculated using the formula: Volume = length × width × depth × 0.525. This formula provides an estimate of the thyroid lobe volume in milliliters (mL). The total thyroid volume is the sum of the volumes of both lobes. A normal total thyroid volume typically ranges from 10 to 20 mL, but this can vary depending on the reference values used by different studies or clinical practices.
Clinical Implications
Understanding the normal size range of the thyroid gland is critical for the diagnosis and management of thyroid diseases. For example, a significantly enlarged thyroid (goiter) may require further investigation to determine its cause, which could range from benign conditions like iodine deficiency to more serious diseases such as thyroid cancer. On the other hand, a smaller-than-expected thyroid size could be indicative of conditions like thyroiditis or surgical removal of part of the thyroid.
FAQ Section
What is considered a normal thyroid size on an ultrasound?
+A normal thyroid lobe is approximately 2 cm in length and about 1.3 to 1.5 cm in width and depth, but these dimensions can vary slightly among individuals.
Can iodine intake affect thyroid size?
+Yes, iodine deficiency is a common cause of thyroid enlargement (goiter). Adequate iodine intake is essential for maintaining a normal thyroid size and function.
How does pregnancy affect thyroid size?
+Due to increased levels of estrogen during pregnancy, the thyroid may become slightly larger. However, significant changes in thyroid size during pregnancy should be evaluated by a healthcare provider.
Why is ultrasound preferred for evaluating thyroid size?
+Ultrasound is non-invasive, does not expose patients to radiation, and is highly sensitive for detecting thyroid nodules and other abnormalities, making it the preferred method for evaluating thyroid size and structure.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the size of the thyroid gland is an important indicator of thyroid health, and understanding what constitutes a normal size is crucial for the accurate diagnosis and management of thyroid diseases. Factors such as iodine intake, age, sex, and underlying thyroid conditions can influence thyroid size, emphasizing the need for personalized evaluation and care. Through the use of ultrasound technology, healthcare professionals can assess thyroid size and structure, providing valuable insights into thyroid health and guiding appropriate treatment strategies. As research continues to evolve, our understanding of thyroid size and its implications for health will become more refined, leading to better outcomes for individuals with thyroid disorders.
