Thyroid Ultrasound Guide: Accurate Measurements
The thyroid gland, a butterfly-shaped endocrine gland located in the neck, plays a vital role in regulating metabolism, energy generation, and overall hormonal balance. Ultrasound technology has become a crucial diagnostic tool for evaluating thyroid health, allowing for the accurate measurement of thyroid size, structure, and potential abnormalities. This guide aims to provide an in-depth exploration of thyroid ultrasound techniques, emphasizing the importance of accurate measurements in diagnosing and managing thyroid-related conditions.
Understanding Thyroid Ultrasound
Thyroid ultrasound is a non-invasive, painless procedure that utilizes high-frequency sound waves to produce detailed images of the thyroid gland. This diagnostic technique is particularly useful for assessing thyroid nodules, cysts, and other abnormalities that may indicate thyroid cancer, hyperthyroidism, or hypothyroidism. By providing real-time images, ultrasound enables healthcare professionals to measure thyroid size, evaluate nodule characteristics, and guide fine-needle aspiration biopsies when necessary.
Accurate Measurements: Key to Diagnosis
Accurate measurements are critical in thyroid ultrasound, as they help differentiate between benign and potentially malignant conditions. The following parameters are typically assessed:
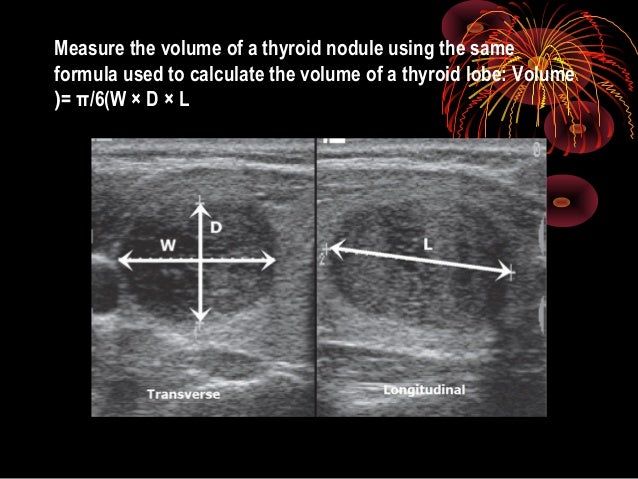
- Thyroid size: Measuring the length, width, and depth of each thyroid lobe helps evaluate overall thyroid volume and detect any asymmetry or abnormal growth.
- Nodule size and characteristics: Assessing the size, shape, composition (cystic, solid, or mixed), and margins of thyroid nodules is essential for determining their potential for malignancy.
- Echogenicity: Evaluating the brightness of thyroid tissue and nodules on ultrasound images helps identify patterns suggestive of specific conditions, such as hypoechogenicity often seen in malignant nodules.
- Vascularity: Analyzing the blood flow within nodules can provide insights into their nature, with some malignant nodules showing increased vascularity.
Standardization of Measurements
Standardizing thyroid ultrasound measurements is vital for ensuring consistency and reliability across different healthcare settings. The American Thyroid Association (ATA) and other professional societies have established guidelines for the performance and interpretation of thyroid ultrasound, including recommendations for measuring thyroid size and nodule characteristics. Adhering to these guidelines helps in reducing variability and improving the accuracy of diagnoses.
Technical Aspects of Thyroid Ultrasound
The technical aspects of performing a thyroid ultrasound involve selecting the appropriate ultrasound equipment and settings. High-frequency linear array transducers (typically 7.5-14 MHz) are preferred for their high resolution, allowing for detailed visualization of the thyroid gland and its structures. Proper patient positioning, usually supine with the neck extended, and the use of a pillow or pad to support the neck can enhance image quality.
Clinical Applications and Interpretation
The clinical applications of thyroid ultrasound are diverse, ranging from the initial evaluation of thyroid abnormalities to the long-term follow-up of patients with known thyroid conditions. Interpreting thyroid ultrasound findings requires a comprehensive understanding of thyroid pathology, including the ability to distinguish between benign and potentially malignant conditions based on ultrasound characteristics.
Limitations and Future Directions
While thyroid ultrasound is a powerful diagnostic tool, it is not without limitations. Operator dependency, difficulty in distinguishing between certain types of nodules, and the potential for false-negative or false-positive findings are challenges that clinicians face. Future advancements in ultrasound technology, such as the development of more sophisticated imaging modalities (e.g., elastography) and artificial intelligence-assisted diagnostic systems, are expected to enhance the accuracy and reliability of thyroid ultrasound examinations.
Practical Considerations for Patients
For patients undergoing a thyroid ultrasound, understanding the procedure and its implications can significantly reduce anxiety and improve compliance. Key points to consider include:
- Preparation: Typically, no specific preparation is required, though patients may be asked to remove jewelry or clothing that could interfere with the ultrasound.
- Procedure: The ultrasound is performed with the patient lying down, and a gel is applied to the neck area to facilitate sound wave transmission.
- Results: Findings are usually discussed with the patient immediately after the procedure, though detailed reports and further consultations may be necessary for comprehensive evaluation and management planning.
Conclusion
Thyroid ultrasound, with its emphasis on accurate measurements, has revolutionized the diagnosis and management of thyroid conditions. By providing detailed, real-time images of the thyroid gland, this non-invasive technique enables healthcare professionals to make informed decisions regarding patient care. As ultrasound technology continues to evolve, its role in thyroid disease management is likely to expand, offering new avenues for early detection, precise diagnosis, and tailored therapeutic interventions.
What is the primary purpose of a thyroid ultrasound?
+The primary purpose of a thyroid ultrasound is to evaluate the size, structure, and abnormalities of the thyroid gland, including nodules, cysts, and potential malignancies.
How is thyroid size measured during an ultrasound?
+Thyroid size is measured by assessing the length, width, and depth of each thyroid lobe, helping to calculate the overall thyroid volume and detect any asymmetry.
What are the limitations of thyroid ultrasound?
+Limitations include operator dependency, difficulty in distinguishing between certain types of nodules, and the potential for false-negative or false-positive findings, highlighting the need for skilled interpretation and possibly additional diagnostic tests.
By integrating cutting-edge technology with clinical expertise, thyroid ultrasound has become an indispensable tool in the management of thyroid health, offering patients and healthcare providers alike a powerful means of diagnosing and treating thyroid-related conditions with precision and care.