U Waves Ecg: Improve Diagnosis With Expert Insights
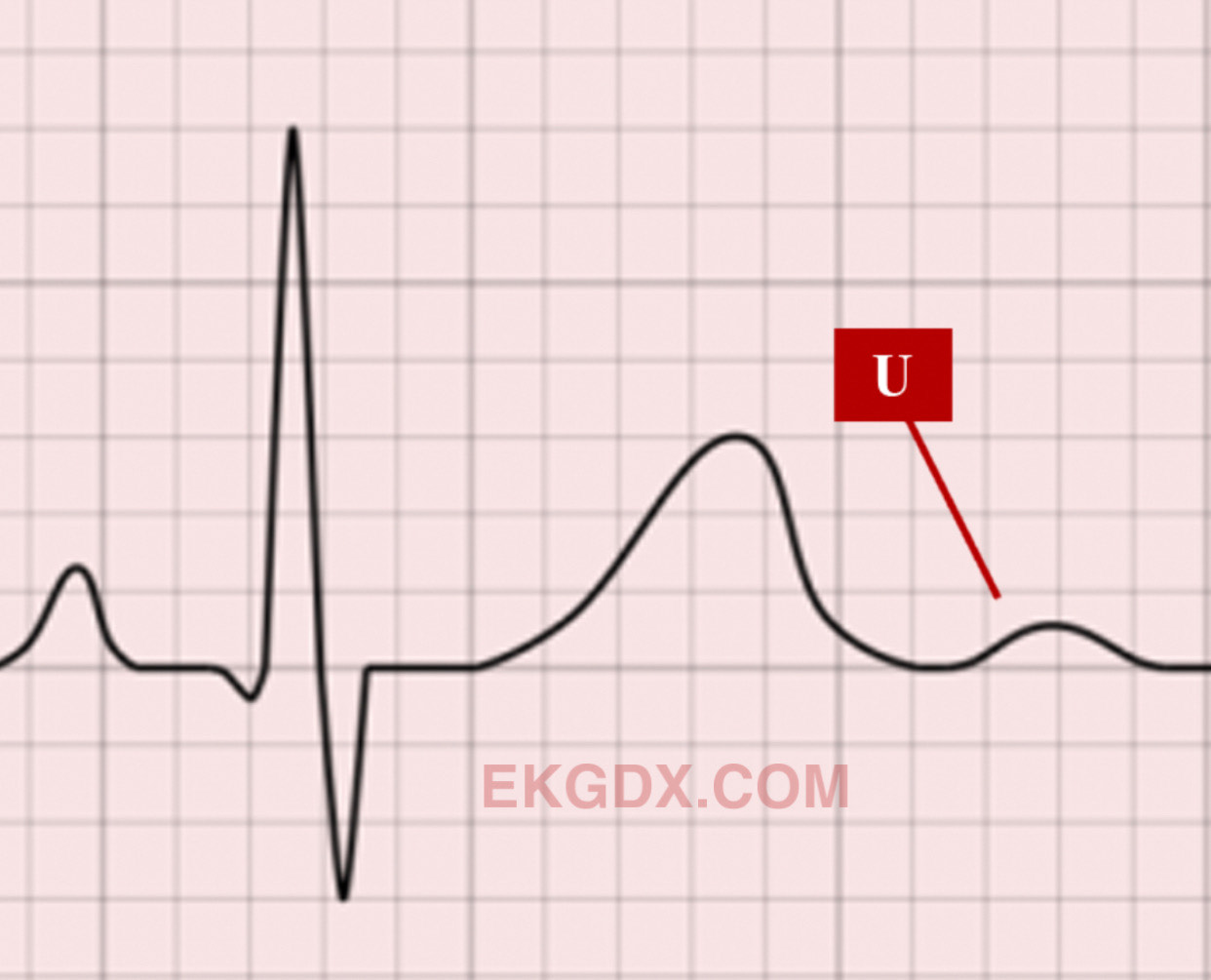
The electrocardiogram (ECG) is a fundamental tool in cardiology, providing valuable insights into the heart’s electrical activity. Among the various components of an ECG, the U wave has garnered significant attention due to its potential to offer diagnostic clues. In this article, we will delve into the world of U waves on ECG, exploring their characteristics, clinical implications, and the expert insights that can refine diagnosis.
Characteristics of U Waves
U waves are low-frequency deflections that appear after the T wave on an ECG, typically in the same direction as the T wave. They are most prominently visible in leads V2 and V3, but can also be observed in other leads, including the limb leads. The U wave is thought to represent the late repolarization of the Purkinje fibers and the ventricular muscle. Studies suggest that U waves are more pronounced in individuals with slower heart rates, as this allows for a more distinct separation from the T wave.
Clinical Implications of U Waves
The presence and characteristics of U waves can provide important diagnostic information. For instance, inverted U waves (those that are opposite in direction to the T wave) have been associated with myocardial ischemia and coronary artery disease. Conversely, prominent U waves can be a marker of hypokalemia (low potassium levels), a condition that can predispose individuals to dangerous arrhythmias. Furthermore, the U wave can be altered in various cardiomyopathies, including hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, where it may be more prominent than usual.
Expert Insights for Enhanced Diagnosis
To fully leverage the diagnostic potential of U waves, it is essential to consider them within the broader context of the patient’s clinical presentation and other ECG findings. Experts recommend the following strategies for improving diagnostic accuracy:
- Holistic ECG Interpretation: Do not isolate the U wave from the rest of the ECG tracing. Consider the entire ECG, including P wave, QRS complex, T wave, and other factors like heart rate and rhythm, to gain a comprehensive understanding of cardiac function.
- Clinical Correlation: Always correlate ECG findings with the patient’s symptoms, medical history, and physical examination. This approach helps to contextualize the significance of U wave abnormalities.
- Technique Optimization: Ensure that the ECG is recorded with optimal technique, including proper electrode placement and a quiet, comfortable environment for the patient, to minimize artifacts and enhance the visibility of U waves.
- Serial ECGs: When possible, compare current ECG findings with previous tracings to detect changes over time, which can be particularly useful in monitoring the progression of cardiac conditions or the effectiveness of treatments.
Problem-Solution Framework: Addressing Diagnostic Challenges
One of the challenges in utilizing U waves for diagnosis is their variability and sensitivity to external factors such as electrolyte imbalances and drug effects. To address these challenges:
- Standardization of ECG Recording: Implement standardized protocols for ECG recording to reduce variability.
- Education and Training: Provide ongoing education and training for healthcare professionals to enhance their skills in ECG interpretation, including the nuances of U wave analysis.
- Integration with Other Diagnostic Tools: Combine ECG findings with information from other diagnostic modalities, such as echocardiography and cardiac MRI, to gain a more complete picture of cardiac function and structure.
Future Trends Projection: Advancements in ECG Technology
The future of ECG diagnosis, including the analysis of U waves, is poised to benefit from advancements in technology. Emerging trends include:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) in ECG Interpretation: AI algorithms can aid in the automated detection and analysis of U waves, potentially improving diagnostic accuracy and speed.
- High-Resolution ECG: Newer ECG systems with higher resolution may enable better visualization of U waves and other subtle ECG findings.
- Personalized Medicine: The integration of genetic information and individual patient characteristics into ECG interpretation may further customize and enhance diagnostic approaches.
Decision Framework for Clinicians
To make informed decisions about the diagnostic utility of U waves, clinicians can follow a structured framework:
- Assess Patient Context: Consider the patient’s overall clinical presentation and medical history.
- Interpret ECG Findings: Analyze the ECG tracing carefully, focusing on the U wave and its characteristics.
- Correlate with Other Findings: Integrate ECG findings with results from other diagnostic tests and clinical evaluations.
- Consult Expert Guidelines: Refer to up-to-date clinical guidelines and expert recommendations for the interpretation of U waves and other ECG abnormalities.
FAQ Section
What are the common causes of inverted U waves on an ECG?
+Inverted U waves can be associated with myocardial ischemia, coronary artery disease, and certain cardiomyopathies. They may also be seen in conditions affecting the repolarization phase of the cardiac cycle.
How do U waves change in hypokalemia?
+In hypokalemia, U waves can become more prominent. This condition can predispose individuals to arrhythmias due to the altered repolarization dynamics.
What is the significance of U waves in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy?
+In hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, U waves may be more pronounced than usual, reflecting the altered repolarization patterns in the hypertrophied myocardium.
In conclusion, U waves on ECG offer valuable diagnostic insights when interpreted within the context of the patient’s overall clinical presentation and with consideration of other ECG findings. By leveraging expert insights, advances in technology, and a holistic approach to ECG interpretation, clinicians can refine their diagnostic accuracy and provide better care for patients with cardiac conditions. As the field continues to evolve, the integration of U wave analysis into daily practice will likely become more sophisticated, contributing to improved patient outcomes.