Vitals In Newborn
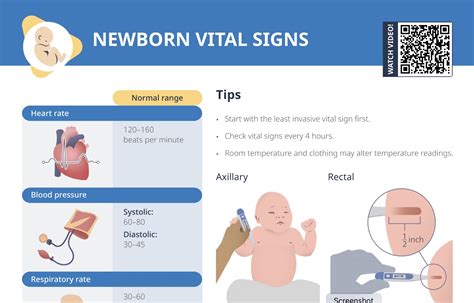
The first few minutes and hours after birth are crucial for a newborn’s health and well-being. Monitoring the newborn’s vital signs is essential to ensure that they are adapting to life outside the womb. The four main vital signs that are typically monitored in newborns are heart rate, respiratory rate, blood pressure, and oxygen saturation.
A normal newborn heart rate is typically between 100 to 160 beats per minute. This can be monitored using a stethoscope or an electrocardiogram (ECG). The heart rate can be influenced by various factors, such as the newborn’s age, weight, and overall health. For example, a premature newborn may have a higher heart rate than a full-term newborn.
The respiratory rate, or the number of breaths per minute, is also an important vital sign in newborns. A normal respiratory rate for newborns is typically between 30 to 60 breaths per minute. This can be monitored by observing the newborn’s chest rise and fall or by using a respiratory monitor. Newborns have a higher respiratory rate than adults because their lungs are smaller and need to work harder to get enough oxygen.
Blood pressure is another vital sign that is monitored in newborns. A normal blood pressure for newborns is typically around 65-90 mmHg systolic and 40-60 mmHg diastolic. This can be monitored using a blood pressure cuff or an invasive blood pressure monitor. Blood pressure can be influenced by various factors, such as the newborn’s age, weight, and overall health.
Oxygen saturation is also an important vital sign in newborns. This measures the amount of oxygen in the blood and is typically monitored using a pulse oximeter. A normal oxygen saturation for newborns is typically above 95%. This can be influenced by various factors, such as the newborn’s age, weight, and overall health.
In addition to these vital signs, newborns are also monitored for other signs of health, such as their temperature, weight, and overall physical condition. A normal newborn temperature is typically between 97.7°F and 99.5°F (36.5°C and 37.5°C). Newborns can lose heat quickly, so it’s essential to keep them warm and cozy.
Newborns are also monitored for their weight, which can influence their overall health and well-being. A normal newborn weight is typically between 5.5 and 8.8 pounds (2.5 and 4 kilograms). Newborns who are underweight or overweight may require special care and monitoring.
Overall physical condition is also an important aspect of newborn health. Newborns are monitored for signs of distress, such as respiratory difficulty, lethargy, or feeding problems. They are also monitored for signs of infection, such as fever, irritability, or feeding problems.
Key Takeaways
- The four main vital signs that are typically monitored in newborns are heart rate, respiratory rate, blood pressure, and oxygen saturation.
- A normal newborn heart rate is typically between 100 to 160 beats per minute.
- A normal respiratory rate for newborns is typically between 30 to 60 breaths per minute.
- Blood pressure and oxygen saturation are also important vital signs in newborns.
- Newborns are also monitored for other signs of health, such as their temperature, weight, and overall physical condition.
How to Monitor Newborn Vitals
Monitoring newborn vitals requires careful attention to detail and the use of specialized equipment. Here are some steps to follow: 1. Use a stethoscope: A stethoscope can be used to listen to the newborn’s heart rate and respiratory rate. 2. Use an electrocardiogram (ECG): An ECG can be used to monitor the newborn’s heart rate and rhythm. 3. Use a respiratory monitor: A respiratory monitor can be used to monitor the newborn’s respiratory rate and oxygen saturation. 4. Use a blood pressure cuff: A blood pressure cuff can be used to monitor the newborn’s blood pressure. 5. Use a pulse oximeter: A pulse oximeter can be used to monitor the newborn’s oxygen saturation. 6. Monitor temperature: Monitor the newborn’s temperature regularly to ensure that it is within a normal range. 7. Monitor weight: Monitor the newborn’s weight regularly to ensure that it is within a normal range. 8. Monitor overall physical condition: Monitor the newborn’s overall physical condition, including signs of distress or infection.
What is a normal heart rate for a newborn?
+A normal newborn heart rate is typically between 100 to 160 beats per minute.
What is a normal respiratory rate for a newborn?
+A normal respiratory rate for newborns is typically between 30 to 60 breaths per minute.
What is a normal blood pressure for a newborn?
+A normal blood pressure for newborns is typically around 65-90 mmHg systolic and 40-60 mmHg diastolic.
What is a normal oxygen saturation for a newborn?
+A normal oxygen saturation for newborns is typically above 95%.
In conclusion, monitoring newborn vitals is an essential aspect of newborn care. By monitoring heart rate, respiratory rate, blood pressure, and oxygen saturation, healthcare providers can quickly identify any potential problems and provide prompt treatment. Additionally, monitoring temperature, weight, and overall physical condition can help ensure that the newborn is healthy and thriving. By following the steps outlined above and using specialized equipment, healthcare providers can provide the best possible care for newborns.

