What Causes High Hb In Newborn? Symptoms Guide
The arrival of a newborn is a momentous occasion, filled with joy and anticipation for the future. However, for some parents, this period can also be marked by concerns over their baby’s health, particularly if they are diagnosed with high hemoglobin (Hb) levels. Hemoglobin is a protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen throughout the body. While it’s crucial for the baby’s overall health, abnormally high levels can indicate underlying issues that need medical attention.
Understanding Hemoglobin in Newborns
In newborns, hemoglobin levels are typically higher than in adults. This is a natural adaptation to the fetal environment, where oxygen levels are lower. Immediately after birth, the baby’s hemoglobin level starts to decrease gradually and reaches adult levels by about 6 months of age. High hemoglobin in newborns, also known as polycythemia, occurs when there is an excessive amount of red blood cells in the blood. This condition can lead to the blood becoming thicker and more viscous, potentially causing complications such as blood clots and poor circulation.
Causes of High Hemoglobin in Newborns
Several factors can contribute to high hemoglobin levels in newborns. Understanding these causes is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment:
Genetic Disorders: Certain genetic conditions can affect the production of red blood cells, leading to polycythemia. For example, mutations in the JAK2 gene can cause an overproduction of red blood cells.
Chronic Hypoxia: Babies who are born at high altitudes or have conditions that lead to chronic hypoxia (low oxygen levels) may produce more red blood cells to compensate for the lack of oxygen.
Placental Insufficiency: If the placenta does not function correctly during pregnancy, it may not provide enough oxygen to the fetus, leading to increased red blood cell production.
Maternal Conditions: Certain conditions in the mother, such as diabetes or smoking during pregnancy, can increase the risk of polycythemia in the newborn.
Twin-to-Twin Transfusion Syndrome: In the case of monochorionic (shared placenta) twins, an imbalance in blood circulation between the two fetuses can lead to one twin having too many red blood cells.
Symptoms of High Hemoglobin in Newborns
While some babies with high hemoglobin levels might not exhibit any symptoms, others may display signs that warrant medical attention. These symptoms can include:
- Respiratory Distress: Difficulty breathing due to poor circulation and increased blood viscosity.
- Cyanosis: A bluish discoloration of the skin due to inadequate oxygenation.
- Feeding Problems: Difficulty feeding due to lethargy or poor sucking reflex.
- Lethargy: Excessive sleepiness or lack of responsiveness.
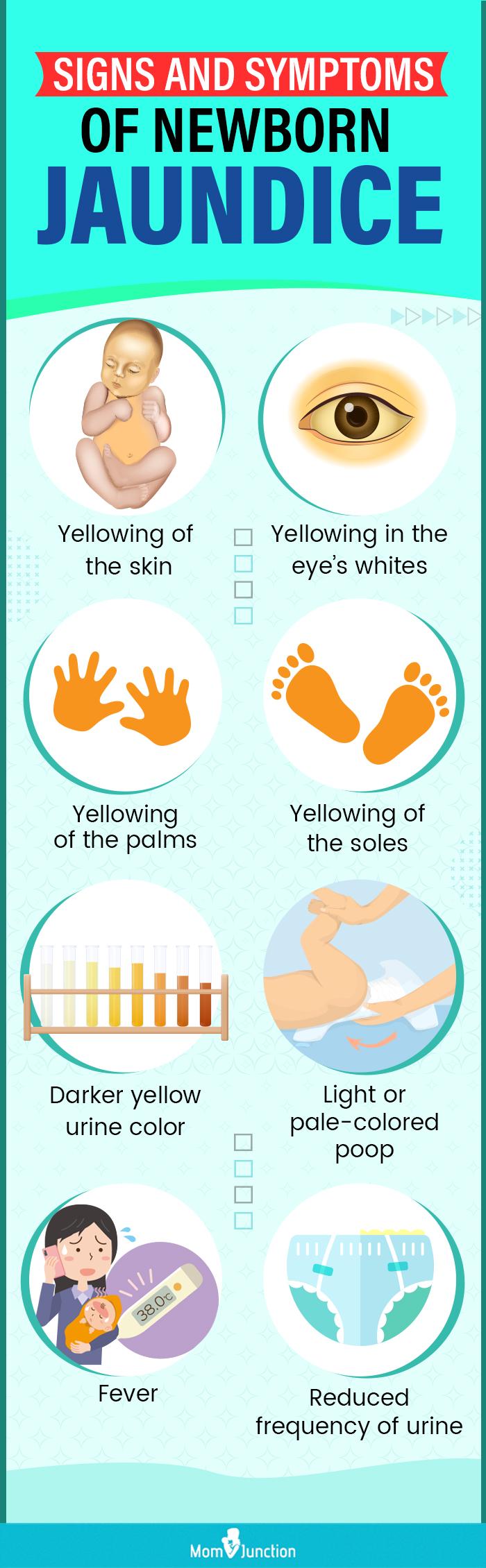
- Jaundice: Elevated bilirubin levels, leading to yellowing of the skin and eyes.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing high hemoglobin in newborns typically involves a complete blood count (CBC) to measure the levels of different blood cells, including hemoglobin. If polycythemia is diagnosed, treatment may involve:
- Partial Exchange Transfusion: Removing some of the baby’s blood and replacing it with a blood product that helps to dilute the blood and improve its flow.
- Phototherapy: For babies with jaundice, phototherapy can help reduce bilirubin levels.
- Monitoring: Close observation of the baby’s condition, including regular blood tests and checks for any signs of complications.
Prevention
While not all cases of high hemoglobin in newborns can be prevented, maintaining a healthy pregnancy and managing any underlying maternal conditions can reduce the risk. This includes:
- Regular Prenatal Care: Attending all scheduled prenatal appointments to monitor both the mother’s and the baby’s health.
- Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Avoiding smoking, maintaining a balanced diet, and managing stress can contribute to a healthier pregnancy.
Conclusion
High hemoglobin levels in newborns, while concerning, can often be managed with appropriate medical care. It’s essential for parents to be aware of the potential causes and symptoms of polycythemia and to work closely with healthcare providers to ensure the best possible outcomes for their baby. With early detection and treatment, many babies with high hemoglobin levels can thrive and develop normally.
What are the common symptoms of high hemoglobin in newborns?
+Common symptoms include respiratory distress, cyanosis, feeding problems, lethargy, and jaundice. However, some babies may not exhibit any noticeable symptoms.
Can high hemoglobin levels in newborns be prevented?
+While not all cases can be prevented, maintaining a healthy pregnancy through regular prenatal care, a balanced diet, and avoiding harmful substances like tobacco can reduce the risk.
How is high hemoglobin in newborns typically treated?
+Treatment may involve partial exchange transfusion to dilute the blood, phototherapy for jaundice, and close monitoring of the baby’s condition. The specific approach depends on the severity of the condition and the presence of any complications.
