What Is Charting In Nursing
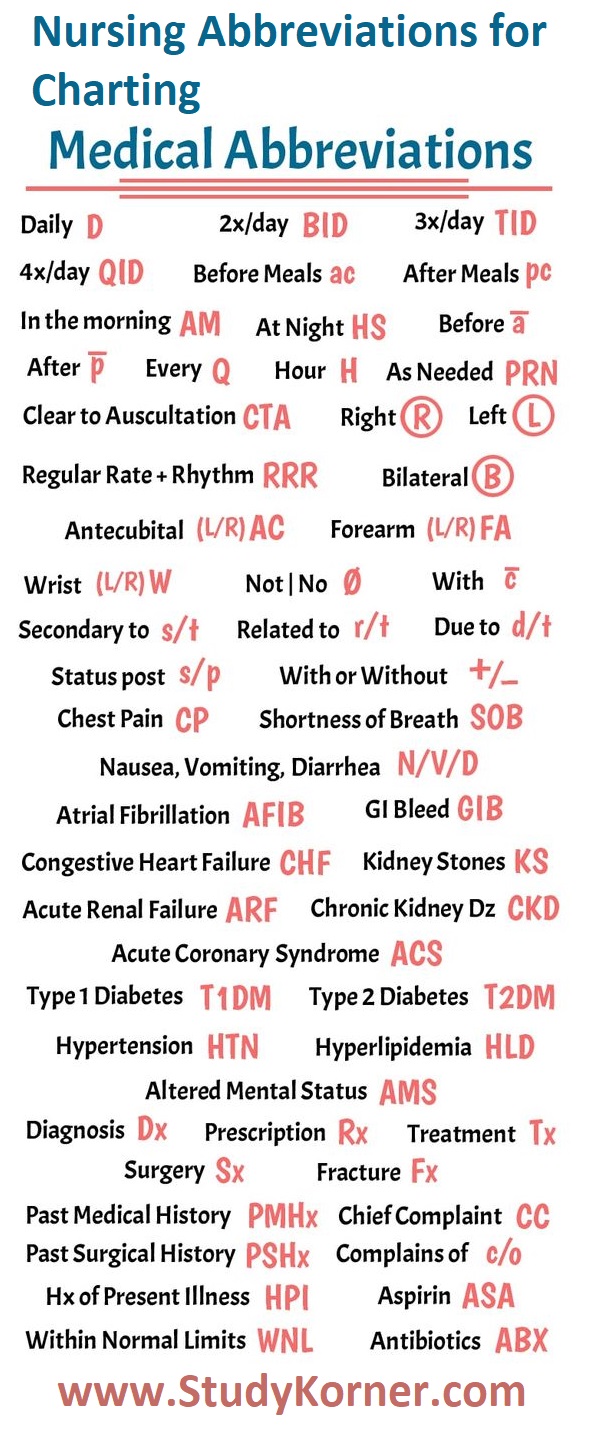
Charting in nursing is a critical process that involves the systematic documentation of a patient’s medical history, treatment, and progress over time. It is a fundamental aspect of nursing practice that serves as a means of communication among healthcare providers, ensuring continuity of care and facilitating informed decision-making. Charting is an essential component of the nursing process, which includes assessment, diagnosis, planning, implementation, and evaluation.
Effective charting in nursing involves the accurate and concise recording of relevant information, including:
- Patient demographics: Name, date of birth, medical record number, and contact information.
- Medical history: Past illnesses, surgeries, allergies, and medications.
- Current symptoms and complaints: Presenting problems, symptoms, and concerns.
- Physical assessment: Vital signs, body systems assessment, and laboratory results.
- Treatment plans: Medications, interventions, and therapies.
- Progress notes: Ongoing assessment, evaluation, and adjustments to the treatment plan.
- Discharge instructions: Patient education, follow-up appointments, and self-care instructions.
The primary goals of charting in nursing are to:
- Ensure continuity of care: Provide a comprehensive and accurate record of a patient’s care, enabling healthcare providers to make informed decisions.
- Facilitate communication: Share information among healthcare providers, promoting collaboration and coordination of care.
- Document patient progress: Track changes in a patient’s condition, response to treatment, and outcomes.
- Enhance patient safety: Identify potential risks, allergies, and sensitivities, reducing the likelihood of adverse events.
- Support quality improvement: Analyze data and identify areas for improvement, driving evidence-based practice and policy development.
There are various methods of charting in nursing, including:
- Source-oriented charting: Organizes information by source, such as laboratory results or medication administration records.
- Problem-oriented charting: Focuses on specific patient problems or diagnoses, with associated interventions and outcomes.
- SOAP charting: Uses a structured format, including Subjective, Objective, Assessment, and Plan, to document patient information.
- Electronic health records (EHRs): Utilize digital platforms to store, manage, and share patient data, enhancing accessibility and efficiency.
Best practices for charting in nursing include:
- Accuracy and completeness: Ensure that all relevant information is recorded accurately and comprehensively.
- Timeliness: Document patient information in a timely manner, ideally at the point of care.
- Legibility: Use clear, concise language and avoid abbreviations or illegible handwriting.
- Standardization: Adhere to established charting protocols and guidelines.
- Confidentiality: Maintain patient confidentiality and adhere to HIPAA regulations.
In conclusion, charting in nursing is a vital process that ensures the delivery of high-quality, patient-centered care. By understanding the principles and best practices of charting, nurses can provide accurate, comprehensive, and timely documentation, ultimately enhancing patient outcomes and improving the overall quality of care.
FAQ Section
What is the primary purpose of charting in nursing?
+The primary purpose of charting in nursing is to ensure continuity of care, facilitate communication among healthcare providers, and document patient progress.
What are the different methods of charting in nursing?
+Common methods of charting in nursing include source-oriented charting, problem-oriented charting, SOAP charting, and electronic health records (EHRs).
What are the best practices for charting in nursing?
+Best practices for charting in nursing include accuracy, completeness, timeliness, legibility, standardization, and confidentiality.

