What Is Intramolecular Force? Easy Explanation
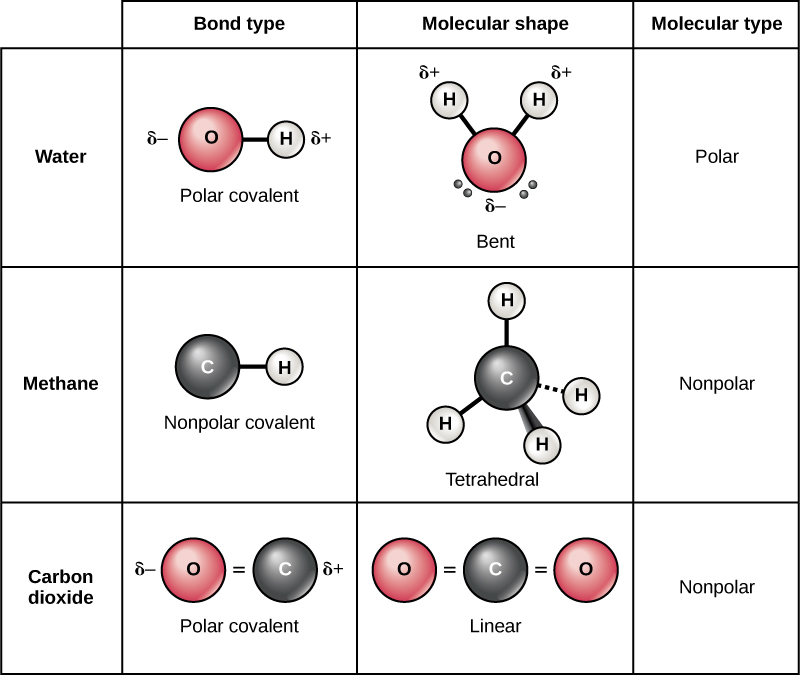
Intramolecular forces are the attractive and repulsive forces that occur within a molecule, influencing its shape, stability, and overall properties. These forces are crucial in understanding the behavior of molecules and their interactions with other molecules. To grasp the concept of intramolecular forces, let’s delve into the different types and their significance.
Types of Intramolecular Forces
Covalent Bonds: These are the strongest intramolecular forces and involve the sharing of electron pairs between atoms. Covalent bonds are responsible for holding the atoms of a molecule together. They can be further classified into sigma (σ) and pi (π) bonds, each with distinct characteristics.
Ionic Interactions: In molecules that contain both positively and negatively charged atoms (ions), ionic interactions can occur. These are not as strong as covalent bonds but are significant in molecules like salts.
Hydrogen Bonds: These are relatively weak forces compared to covalent bonds but play a crucial role in the structure and properties of molecules, especially those with hydrogen atoms bonded to highly electronegative atoms (such as oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine). Hydrogen bonds are pivotal in the structure of water, DNA, and proteins.
Van der Waals Forces: This category includes forces like dipole-dipole interactions, dipole-induced dipole interactions, and induced dipole-induced dipole (London dispersion) forces. Van der Waals forces are weaker than the aforementioned forces but are important in understanding the physical properties of molecules, such as boiling and melting points.
Impact of Intramolecular Forces
Intramolecular forces have profound effects on the physical and chemical properties of molecules. For instance:
Molecular Shape: The arrangement of atoms in a molecule, which is influenced by intramolecular forces, dictates its shape. This shape, in turn, affects how molecules interact with each other and their biological activity.
Solubility: The ability of a substance to dissolve in a solvent is influenced by its intramolecular forces. Polar molecules, which have a separation of charge due to differences in electronegativity, tend to dissolve in polar solvents due to favorable dipole-dipole interactions.
Melting and Boiling Points: The strength of the intramolecular forces within a substance influences its melting and boiling points. Substances with stronger forces between their molecules require more energy to overcome these attractions, resulting in higher melting and boiling points.
Chemical Reactivity: The strength and type of intramolecular forces can influence a molecule’s reactivity. For example, the double bonds in alkenes (which involve both σ and π bonds) are more reactive than single bonds due to the additional electron density in the π bond.
Conclusion
In conclusion, intramolecular forces are critical in understanding the properties and behaviors of molecules. They dictate the structure, stability, and reactivity of molecules, influencing how substances interact with each other and their environment. The complexity and diversity of intramolecular forces highlight the intricate nature of molecular interactions and underscore their importance in chemistry and related fields.
Practical Applications
The study of intramolecular forces has numerous practical applications across various industries:
Drug Design: Understanding the intramolecular forces within drug molecules and their targets (like proteins) is crucial for designing effective drugs with minimal side effects.
Materials Science: The physical properties of materials, such as strength, elasticity, and conductivity, are influenced by intramolecular forces. This understanding is pivotal in developing new materials with specific properties.
Environmental Science: The solubility and reactivity of pollutants in the environment are often dictated by their intramolecular forces, affecting their fate and impact on ecosystems.
Future Perspectives
As our understanding of intramolecular forces continues to evolve, so too will our ability to manipulate and engineer molecules for specific applications. Advances in computational chemistry and experimental techniques are expected to provide deeper insights into these forces, enabling the design of molecules with tailored properties for use in fields from medicine to energy storage.
What role do intramolecular forces play in drug efficacy?
+Intramolecular forces play a significant role in drug efficacy. They influence the drug's ability to bind to its target, its solubility, and its stability, all of which are critical factors in determining how effectively a drug can perform its intended function within the body.
How do intramolecular forces affect the melting point of a substance?
+The melting point of a substance is directly affected by the strength of its intramolecular forces. Substances with stronger intramolecular forces require more energy (higher temperatures) to overcome these forces and transition from a solid to a liquid state, resulting in higher melting points.
What is the difference between intermolecular and intramolecular forces?
+Intramolecular forces occur within a molecule and are responsible for its structure and properties. Intermolecular forces, on the other hand, occur between molecules and influence the physical properties of a substance, such as its boiling and melting points, and its solubility.
In summary, intramolecular forces are fundamental to our understanding of molecular behavior and properties. Their impact is felt across a wide range of scientific disciplines and practical applications, from the design of new materials and drugs to our comprehension of environmental and biological processes. As research continues to illuminate the intricacies of these forces, we can anticipate significant advances in our ability to tailor molecules for specific needs, driving innovation and solving complex challenges.


