What Is The Difference Between Afib And Svt
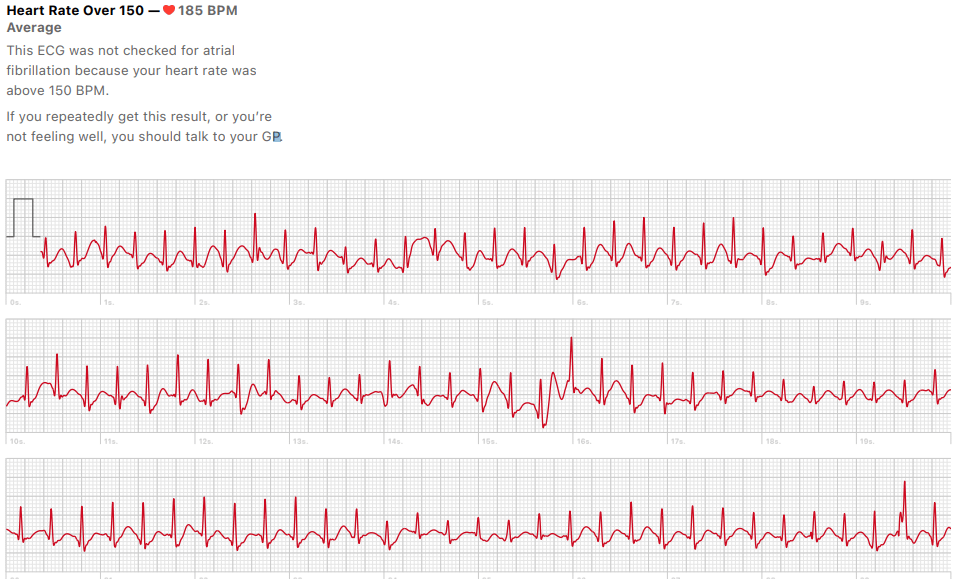
Atrial fibrillation (Afib) and supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) are both cardiac arrhythmias, but they differ significantly in their mechanisms, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment. Understanding these differences is crucial for accurate management and patient outcomes.
Mechanisms and Origins
Afib arises from disorganized electrical signals in the atria, often originating from the pulmonary veins or other focal points. This chaos leads to rapid, irregular atrial contractions, causing the atria to quiver instead of contracting effectively.
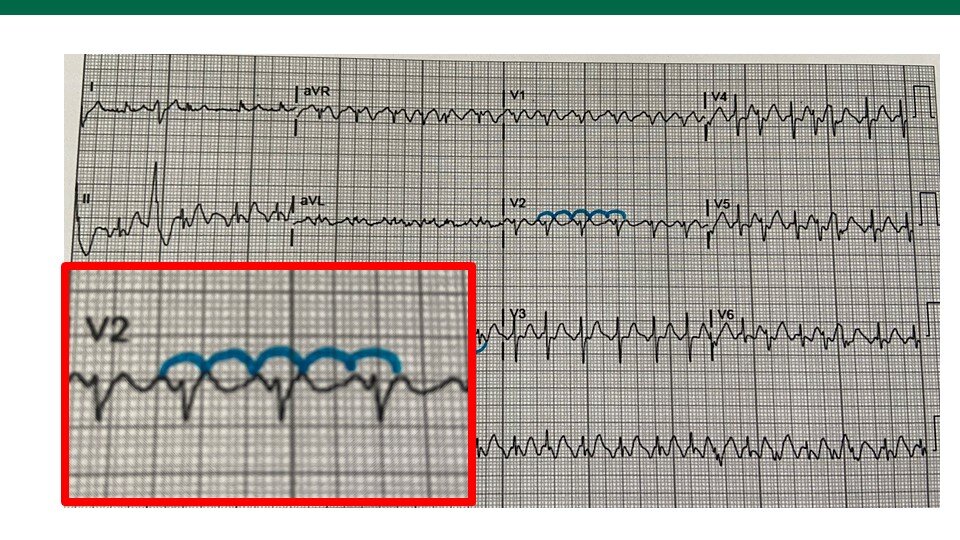
SVT, on the other hand, is a broad term encompassing various arrhythmias originating above the ventricles. The most common type, atrioventricular nodal reentrant tachycardia (AVNRT), involves a reentrant circuit within or near the AV node. Other forms include atrioventricular reentrant tachycardia (AVRT), which relies on an accessory pathway bypassing the AV node.
Symptoms and Presentation
Afib Symptoms:
- Palpitations (awareness of rapid heartbeat)
- Fatigue and weakness
- Shortness of breath, especially during exertion
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Chest discomfort or pain
- Reduced exercise tolerance
SVT Symptoms:
- Sudden onset of rapid heartbeat (often regular)
- Palpitations
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Shortness of breath
- Anxiety or panic
- Rarely, chest pain or syncope (fainting)
While both conditions share some symptoms, SVT episodes typically have a sudden onset and offset, whereas Afib symptoms may be more persistent or intermittent.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis relies on electrocardiogram (ECG) findings:
- Afib: Irregularly irregular rhythm, absence of distinct P waves, and variable R-R intervals.
- SVT: Narrow complex tachycardia (QRS duration < 120 ms), regular rhythm, and often visible P waves (may be retrograde or obscured).
Additional tests like Holter monitoring, event monitoring, or electrophysiology studies may be necessary for confirmation and subtype classification.
Treatment Approaches
| Treatment | Afib | SVT |
|---|---|---|
| Acute Management | Rate control (beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers) or rhythm control (antiarrhythmics, electrical cardioversion) | Vagal maneuvers, adenosine, calcium channel blockers, beta-blockers, or electrical cardioversion |
| Long-Term Management | Anticoagulation (to prevent stroke), rate or rhythm control, lifestyle modifications | Antiarrhythmics, beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, catheter ablation (for recurrent episodes) |
Key Takeaways
- Afib is characterized by irregular atrial activity, while SVT typically presents with a regular, narrow complex tachycardia.
- Afib often requires long-term anticoagulation due to stroke risk, whereas SVT generally does not.
- While both conditions can cause palpitations and shortness of breath, SVT episodes are usually abrupt in onset and offset, unlike Afib.
- Treatment strategies differ significantly, emphasizing the importance of accurate diagnosis.
FAQ Section
Can Afib and SVT occur together?
+Yes, it's possible for individuals to have both conditions. In such cases, management becomes more complex, requiring careful consideration of both arrhythmias.
Which condition is more serious, Afib or SVT?
+Both conditions can be serious, but Afib poses a higher risk of stroke and heart failure due to its chronic nature and potential for complications. SVT episodes are typically less dangerous but can be distressing and impact quality of life.
Can lifestyle changes help manage Afib and SVT?
+Yes, lifestyle modifications like maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, managing stress, limiting caffeine and alcohol, and quitting smoking can significantly improve symptoms and reduce the frequency of episodes in both conditions.
Is catheter ablation a cure for Afib or SVT?
+Catheter ablation can be highly effective in treating both conditions, offering long-term relief from symptoms. However, it's not always a permanent cure, and recurrence is possible. Success rates vary depending on the type of arrhythmia and individual factors.
How can I tell the difference between Afib and SVT at home?
+While it can be challenging to differentiate without an ECG, SVT episodes typically have a sudden onset and offset, with a regular rhythm. Afib symptoms may be more persistent or intermittent, and the pulse often feels irregular. Consulting a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis is essential.
In conclusion, while Afib and SVT share some similarities, they are distinct arrhythmias with unique characteristics. Accurate diagnosis is crucial for appropriate management and optimal patient outcomes. Understanding the differences between these conditions empowers healthcare professionals and patients to make informed decisions regarding treatment and lifestyle modifications.