What's My Nuclear Bomb Radius? Safety Zone Map
The devastating impact of a nuclear bomb is a stark reminder of the importance of global peace and safety. When considering the effects of such a catastrophic event, it’s crucial to understand the nuclear bomb radius and the subsequent safety zones that are established to protect human life and minimize damage.
To determine the radius of a nuclear bomb’s impact, several factors must be considered, including the bomb’s yield, which is a measure of the amount of energy released during the explosion, the altitude at which the bomb is detonated, and the environmental conditions of the area, such as weather patterns and the presence of buildings or other structures that could affect the blast’s impact.
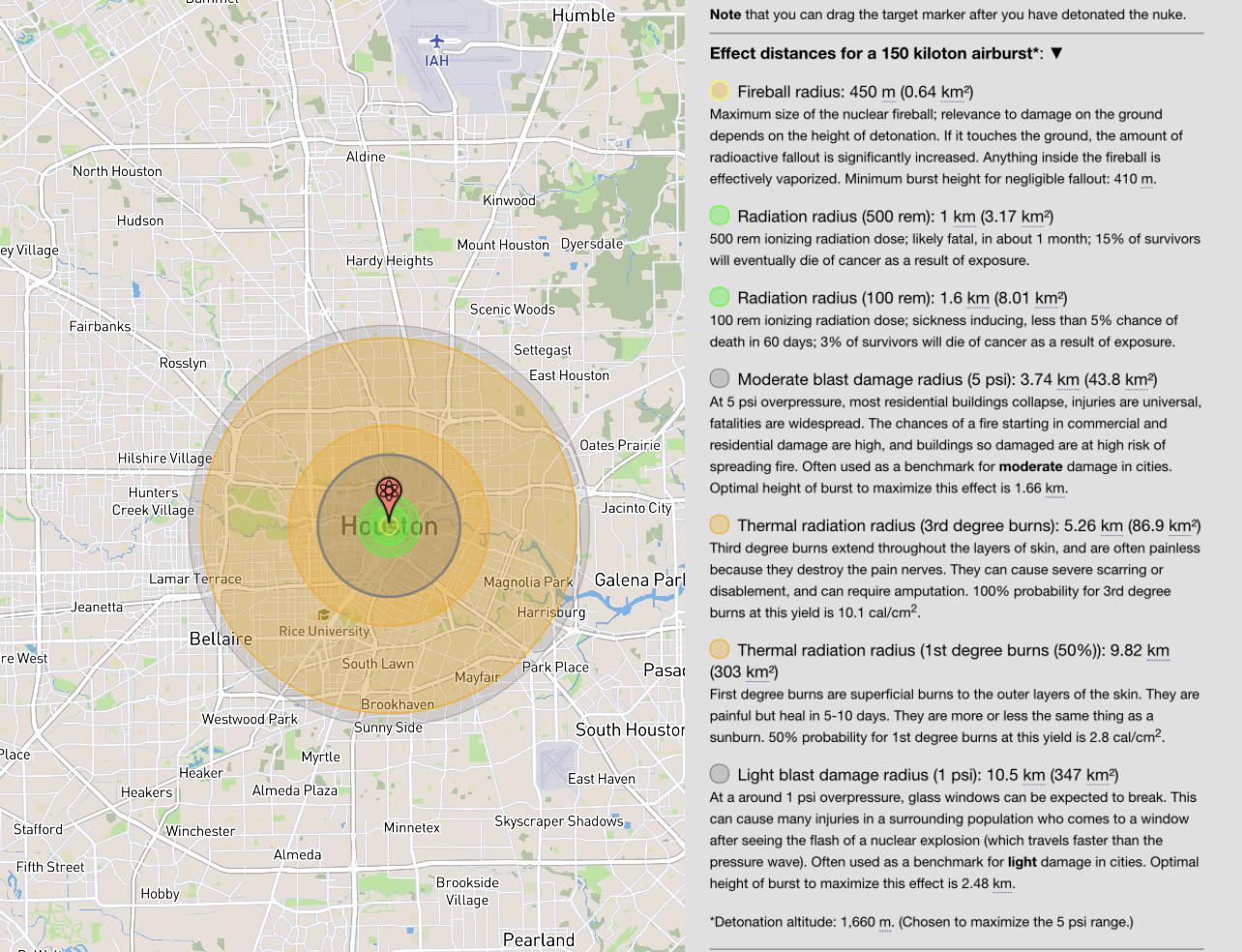
The immediate effects of a nuclear explosion can be divided into several zones, each with distinct characteristics and levels of destruction. The first zone is the hypocenter, which is the area directly beneath the point of detonation. This area is completely devastated, with everything being vaporized or melted due to the extreme heat generated by the explosion.
Surrounding the hypocenter is the fireball, an area where the heat is so intense that it causes widespread fires and burns. The radius of the fireball depends on the yield of the bomb but can extend for several miles. Moving outward, the next zone is the blast area, where the shockwave from the explosion causes significant damage to structures and can lead to fatalities due to flying debris and collapsing buildings.
Beyond the blast area is the radiation zone, where people can be exposed to lethal doses of radiation. This zone can extend much further than the blast area, depending on the wind direction and speed, and can have long-term health effects on those exposed.
To create a safety zone map, one must consider these factors and zones. The map would typically include the following elements:
- Blast Zone: This area would be divided into sub-zones based on the severity of the blast’s impact, with the closest areas to the hypocenter experiencing total destruction and farther areas experiencing progressively less damage.
- Thermal Radiation Zone: This zone indicates areas where thermal radiation from the fireball could cause burns or start fires.
- Ionizing Radiation Zone: This area highlights the regions where ionizing radiation could pose a significant threat to human health, including acute radiation syndrome and increased risk of cancer.
- Fallout Zone: For bombs that are detonated at a low altitude, radioactive fallout becomes a significant concern. This zone would show the areas where radioactive particles could fall to the ground, contaminating the environment.
Creating such a map requires sophisticated modeling and data, including the exact yield of the nuclear device, the detonation altitude, and detailed information about the terrain and weather conditions of the affected area.
For those looking to understand their proximity to potential nuclear threats or wishing to plan emergency response strategies, utilizing online nuclear bomb radius calculators can provide a general idea of the potential impact zones based on the yield of the device and the distance from the detonation point. However, these tools should be used with caution, recognizing their limitations in predicting the actual effects of a nuclear explosion, which can be significantly influenced by a myriad of factors.
In the event of a nuclear emergency, following the guidelines and instructions provided by local authorities and emergency response teams is crucial. These organizations have access to detailed information and resources that can help minimize risks and ensure safety.
Understanding the potential impacts of a nuclear bomb and the safety zones that are crucial for protecting life and property is a step towards mitigating the risks associated with such weapons. As the world continues to navigate the complexities of nuclear disarmament and global security, enhancing our knowledge and preparedness for any eventuality is paramount.
FAQs:
What factors determine the radius of a nuclear bomb's impact?
+The yield of the bomb, the altitude at which it is detonated, and environmental conditions such as weather and the presence of structures are key determinants of the nuclear bomb radius.
How is a safety zone map for a nuclear bomb created?
+A safety zone map considers the blast zone, thermal radiation zone, ionizing radiation zone, and fallout zone, requiring detailed modeling and data on the bomb's yield, detonation altitude, terrain, and weather conditions.
What should I do in the event of a nuclear emergency?
+Follow the instructions provided by local authorities and emergency response teams. They have the necessary information and resources to help minimize risks and ensure safety.
The threat of nuclear weapons is a stark reminder of the importance of peace, diplomacy, and international cooperation. While understanding the effects of a nuclear bomb and planning for safety are critical, the ultimate goal remains the prevention of such catastrophic events through global unity and the pursuit of peace.


